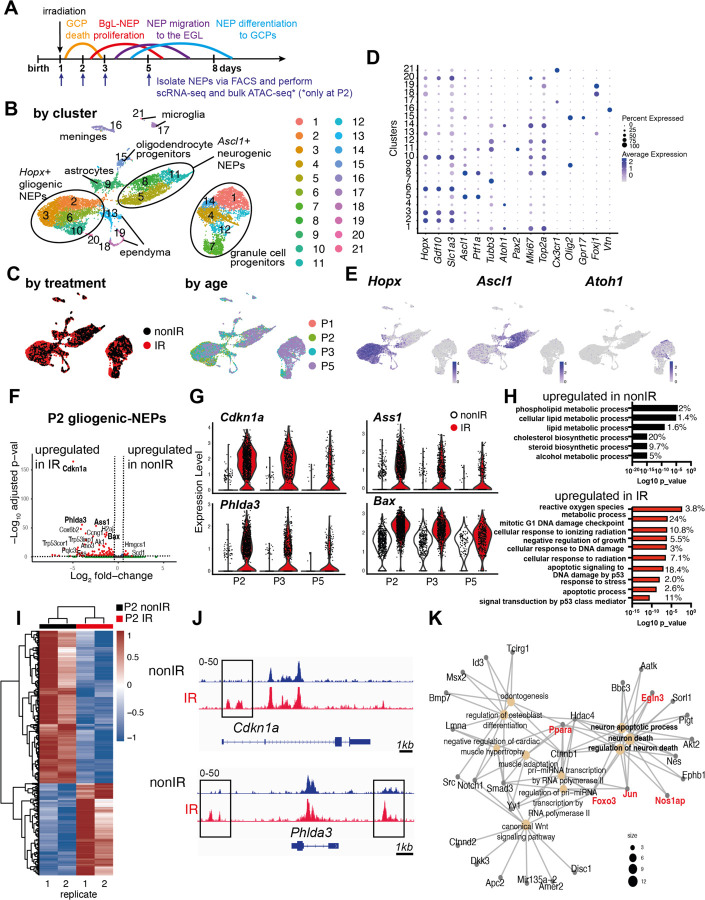
Figure 1: Injury induces ROS and cell stress signaling reflected by changes in the transcriptome and chromatin landscape of gliogenic-NEPs.
(A) Schematic summarizing the experimental plan.
(B-C) UMAP projections of 11,878 cells (6,978 nonIR and 4,900 IR) showing cluster annotations (B), treatment (black: nonIR, red: IR) and the age of the samples (red: P1, green: P2, blue: P3, purple: P5) (C).
(D) Dot plot showing the expression levels of key marker genes used for cluster annotation (gliogenic-NEPs: Hopx, Gdf10, Slc1a3, neurogenic-NEPs: Ascl1, Ptf1a, immature neurons: Pax2, GCPs: Atoh1, postmitotic neurons: Tubb3, microglia: Cx3cr1, oligodendrocyte progenitors: Olig2, oligodendrocytes: Gpr17, Ependymal cells: Foxj1).
(E) Feature plots showing Hopx (gliogenic-NEPs), Ascl1 (neurogenic-NEPs) and Atoh1 (GCPs) expression highlighting the three main populations of interest. Clusters containing Hopx-NEPs (clusters 2, 3, 6, 10), Ascl1-NEPs (clusters 5, 8, 11), or GCPs (clusters 1, 4, 7, 12, 14) were subsetted from the original data set and were divided according to age (P2 or P3+P5) for the downstream differential expression analyses.
(F) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes in the P2 gliogenic-NEPs (red: adjusted p-value≤0.05, log2fold-change>|1|).
(G) Violin plots showing some of the top differentially expressed genes in P2 gliogenic-NEPs and how their expression changes over time with respect to their expression in control cells.
(H) Top GO terms associated with differentially expressed genes in P2 gliogenic-NEPs that were either upregulated in nonIR (top panel) or IR (bottom panel) cells (adjusted p-value≤0.05, Table S3).
(I) Heatmap showing differentially open chromatin regions in P2 nonIR and IR NEPs, identified by bulk ATAC-seq (1168 differentially open regions, adjusted p-value<0.05, Table S4).
(J) Tracks highlighting the injury-induced open chromatin regions around Cdkn1a and Phlda3, the top differentially expressed genes identified in (F).
(K) Gene network analysis of ATAC-seq data revealed an active transcriptional network involved in regulating cell death and apoptosis. Genes colored in red (Ppara, Egln3, Foxo3, Jun and Nos1ap) have been implicated as upregulated with increased ROS levels or involved in ROS signaling.