Figure 5.
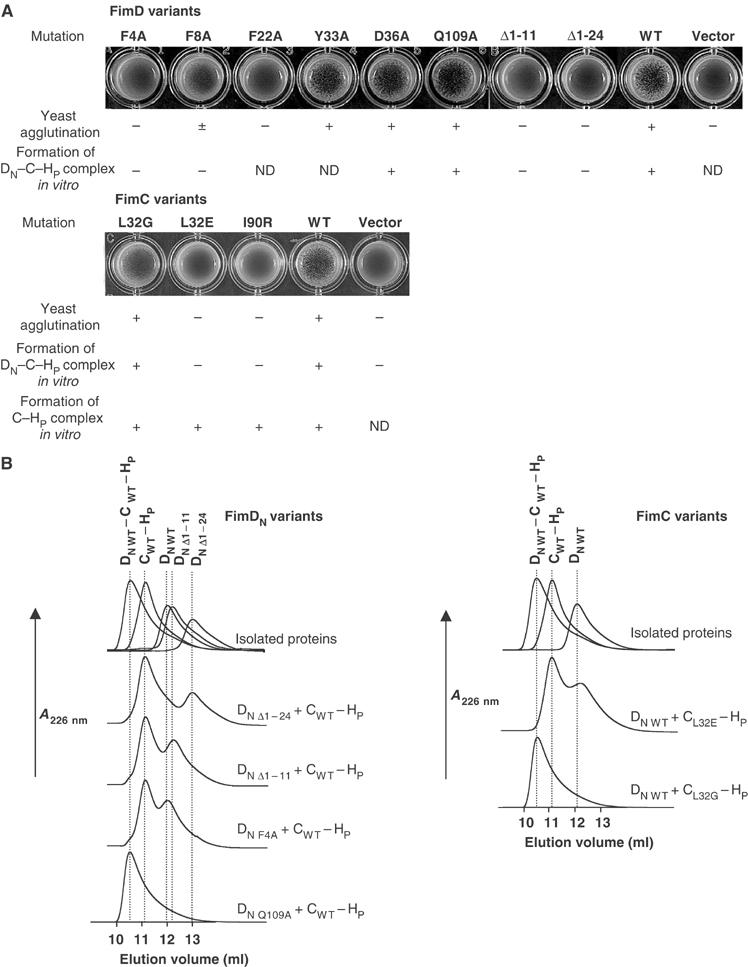
Analysis of amino-acid replacements and deletions in FimD, FimDN(1–139), and replacements in FimC with respect to type 1 pilus biogenesis in vivo and formation of ternary FimDN(1–139)–FimC–FimHP complexes in vitro. (A) Yeast agglutination assays, probing the formation of functional type 1 pili through agglutination with yeast cells. The E. coli strains W3110ΔfimD and W3110ΔfimC were transformed with expression plasmids carrying the indicated FimD and FimC variants, respectively. Agglutination intensities are indicated as (−) no agglutination, (±) weak or (+) strong. The ability of FimDN(1–139) and FimC variants to form the ternary complex as well as the ability of FimC variants to bind FimHP in vitro are indicated as ‘yes' (+) or ‘no' (–). ND, not determined. (B) Analytical gel filtration at pH 7.4 and 25°C, probing the effect of mutations in FimDN(1–139) or FimC on the formation of the FimDN(1–139)–FimC–FimHP complex.
