Figure 4.
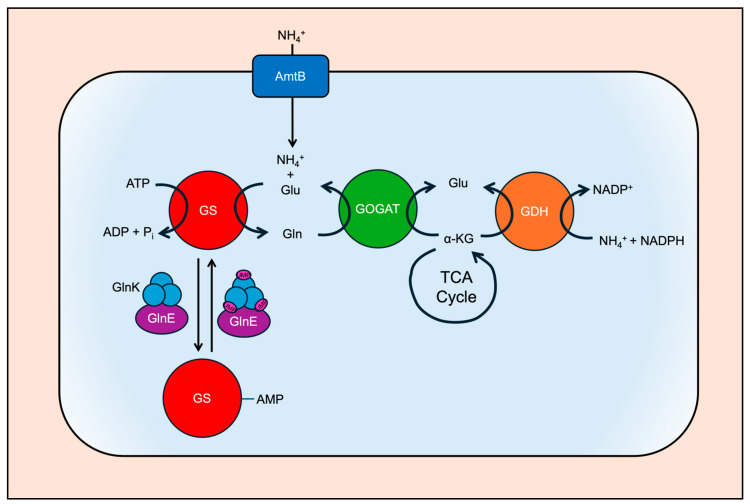
Nitrogen assimilation pathways in bacteria. Ammonium ions are transported into cells through Amt B, and it can then be utilized by either glutamine synthetase (GS) or glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) to produce glutamine or glutamate, respectively. Glutamine can be utilized as a nitrogen donor to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) to produce glutamate. Glutamine synthetase is reversibly modified by GlnE based on GlnK’s uridylyation status. In plants, ammonia is assimilated in the cytoplasm or chloroplast by GS. Ammonia can be uptaken by the roots and, in some species, produced in the mitochondria from photorespiration and proposed to passively move to the cytoplasm.