Table 4.
Characteristics of the nano-drugs and the in vitro thrombotic and fibrinolytic activity of these nano-drugs compared to their respective non-conjugated fibrinolytic activator alone.
| Nano-Drugs | Characteristics | Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
PEGylation
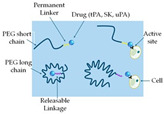
|
PEG-tPA PEG-UK PEG-SK PEG-SAK PEG-maleimide-(poly-SAK) |
Reduced proteolytic activity Slower inhibition kinetics by PAI-1 Increased fibrinolysis Resistant to plasmin cleavage Increased fibrinolysis Slightly increased fibrinolysis Increased bioactivity |
[131] [132] [133,134] [135] [136] |
Liposome
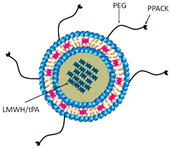
|
A circular-shaped diacyl-chain phospholipids/phospholipid-attached PEG with cholesterol
|
Reduce thrombus weight Improve thrombolytic efficacy, reduce tPA-induced hemorrhage Prolong inhibition of thrombosis, reduced systemic side effects |
[137] [138] [139,140] |
Echogenic liposome and polymeric nanoparticles
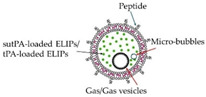
|
tPA-loaded ELIPs NIR-stimulated uPA release Magnetic nanoparticles Ultrasound-guided RDG-modified ELIPs |
Enhance thrombolytic efficiency Significant thrombolysis Prolong circulating tPA Improve thrombolytic efficacy Minimize off-target effects Similar thrombolysis, reduce the dose of tPA Complete thrombus elimination Effective thrombolysis in a rat embolism model Enhanced thrombolytic efficacy of tPA Improve recanalization rate |
[141,142,143] [144] [145] [141,146,147] [148] [148] [149] [150] [151] [152] |
Dendrimer
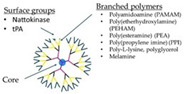
|
tPA-dendrimer complex Nattokinase–dendrimer complex LMWH–dendrimer complex Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers Poly(lysine) dendrimers |
High clot-dissolving activity Effective thrombolytic effect Prevents DVT Induce fibrinogen aggregation, contribute to the in vivo DIC, produce rapid coagulation Ideal carriers of protein drugs |
[153] [154] [155,156] [157] [158] [156] |
Mechanically activated nanotherapeutics
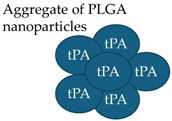
|
tPA-PLGA shear-activated nanoparticle (tPA-SA-NP) complex tPA-loaded SA-NP and temporary endovascular bypass (TEB) |
Rapid clot dissolution Increase recanalization, reduce distal embolization |
[159,160] [161,162] [163] |
Platelet-based drug delivery system
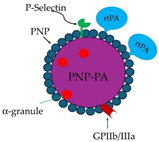
|
rtPA-PNP-PA | Thrombolysis | [164] |
