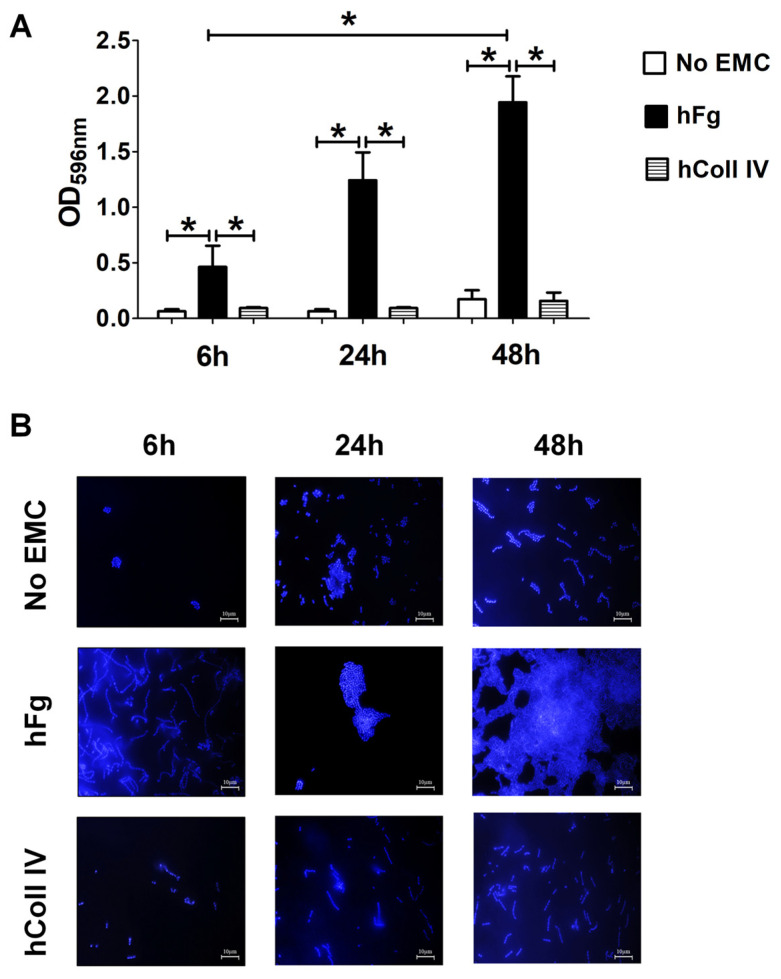
Figure 1.
Biofilm formation by GBS on human fibrinogen. (A) Biofilm formation abilities of NEM316 wild-type (WT) strain on twelve-well plates coated with human fibrinogen (hFg) and collagen type IV (hColl IV) or without any extracellular matrix component (no EMC). GBS growth as biofilm was followed for 6, 24, and 48 h and verified with CV staining. Bacterial biomass was quantified by measuring the optical density at 596 nm (OD596nm). Results are means ± SD from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. * p < 0.05, as determined by Mann–Whitney statistical analysis. (B) Fluorescence microscopy analysis of GBS biofilm morphology over hFg. After growth in the conditions described in A, biofilms were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue), which labeled DNA. In the absence of extracellular matrix components (no EMCs) or in the presence of hColl IV, only few and small scattered cell clusters or small aggregates are visible. In hFg-coated coverslips, a network of numerous, thick cell layers and shaped, rough biofilms are observed. Shown are representative images of three independent experiments. Scale bar = 10 µm.