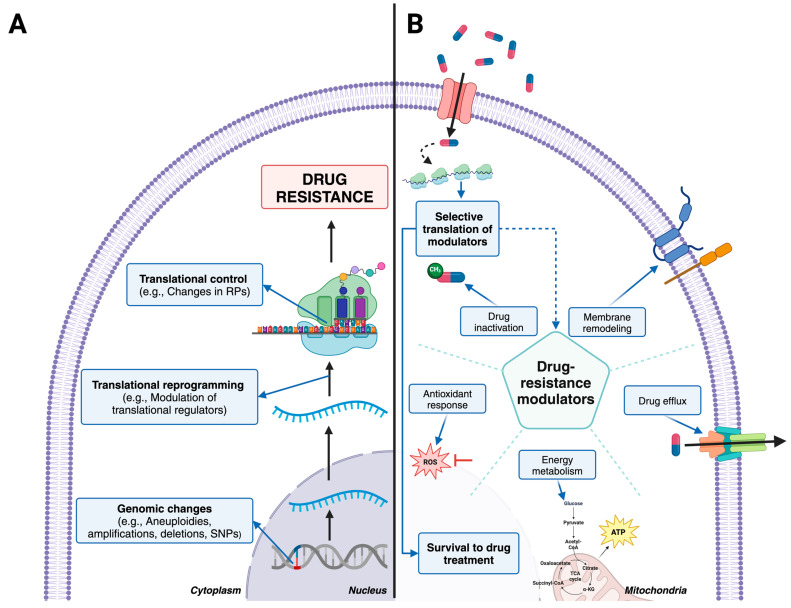
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in Leishmania. (A) Mechanisms employed by Leishmania to develop drug resistance involve changes at the genomic and translational levels. Resistant parasites possess a remodeled translational profile that is distinct from profile of sensitive parasites even in the absence of the antimony drug, which serves as a pre-emptive adaptation to drug challenge. (B) This depicts the response of drug-resistant parasites to drug challenge. Once the resistant parasite recognizes the presence of the drug, it activates the selective translation of mRNAs encoding drug-resistance modulators. These modulators are involved in various response mechanisms, such as surface protein remodeling, drug efflux, the optimization of the energy metabolism, antioxidant response, and drug inactivation. Together, these mechanisms act quickly and in a coordinated manner to combat treatment.