Abstract
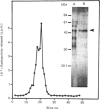
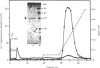
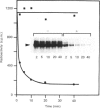
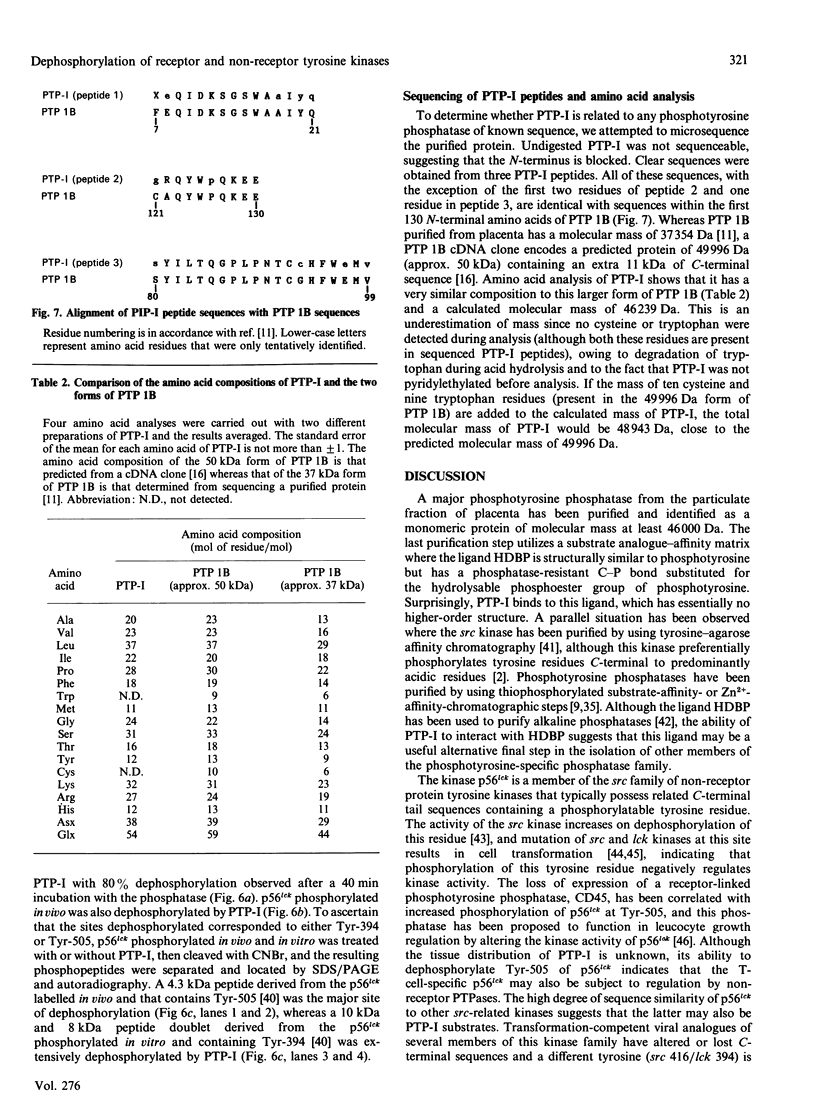
Purification of a major placental membrane protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase (PTP-I) through the use of a nonhydrolysable phosphotyrosine analogue affinity ligand has enabled identification of the enzyme as a single polypeptide of at least 46 kDa. This phosphatase specifically dephosphorylates phosphotyrosine-containing substrates, including the src peptide, the epidermal-growth-factor receptor tyrosine kinase and the non-receptor tyrosine kinase p56lck. The p56lck can be dephosphorylated by PTP-I at two tyrosine residues (Tyr-394 and Tyr-505), which are differentially phosphorylated in vitro and in vivo and have been suggested to modulate kinase activity. The activity of PTP-I towards these substrates indicates a possible function of regulation of cellular tyrosine phosphorylation pathways at the level of growth-factor receptor and/or oncogene/proto-oncogene tyrosine kinases. Kinetic analyses show that PTP-I exhibits a Km value of about 2 microM with either src peptide or reduced, carboxyamidomethylated and maleylated (RCM)-lysozyme as substrate, and is inhibited in a mixed competitive manner by the polyanions heparin and poly(Glu4,Tyr1). Sequencing of PTP-I peptides reveals almost complete identity with sequences within the N-terminal half of the 37 kDa non-receptor tyrosine phosphatase 1B. However, the size and amino acid composition of PTP-I are similar to that of a higher-molecular-mass form of PTP 1B predicted from cDNA cloning. These results suggest that the 37 kDa PTP 1B is a proteolysed form of PTP-I, and provide evidence that a larger form of PTP 1B exists in vivo, at least in association with placental membranes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Veillette A., Schwartz A. M., Deseau V., Rosen N. Analysis of pp60c-src in human colon carcinoma and normal human colon mucosal cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):149–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E. Sites of in vivo phosphorylation of the T cell tyrosine protein kinase in LSTRA cells and their alteration by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9859–9864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. P., Gallis B., Blumenthal D. K., Pallen C. J., Wang J. H., Krebs E. G. Characterization of the phosphotyrosyl protein phosphatase activity of calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9890–9895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. R., Stinson R. A. Dephosphorylation of phosphoproteins of human liver plasma membranes by endogenous and purified liver alkaline phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7635–7639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Kumar S., Diltz C. D., Harrylock M., Cool D. E., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Human placenta protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: amino acid sequence and relationship to a family of receptor-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H. The leukocyte common antigen (CD45): a putative receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff J., Schievella A. R., Jost C. A., Erikson R. L., Neel B. G. Cloning of a cDNA for a major human protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Fagard R., Boulet I., Gesquière J. C. The amino terminal region of the p56 lck from LSTRA exerts negative modulation on the tyrosine kinase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):819–826. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami Y., Lipmann F. Purification of the Rous sarcoma virus src kinase by casein-agarose and tyrosine-agarose affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):321–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Pallen C. J., Parker P. J., Hermann J., Waterfield M. D., Merlevede W. Conversion of a phosphoseryl/threonyl phosphatase into a phosphotyrosyl phosphatase. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):1029–1034. doi: 10.1042/bj2561029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W., Lu D. J., Mills G. B. Vanadate stimulates oxygen consumption and tyrosine phosphorylation in electropermeabilized human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):318–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Haun R. S., Watson S. J., Geahlen R. L., Dixon J. E. Cloning and expression of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson R. L., Ingebritsen V. M., Ingebritsen T. S. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatases. I. Separation of multiple forms from bovine brain and purification of the major form to near homogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7747–7753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K. Transformation of cells by an inhibitor of phosphatases acting on phosphotyrosine in proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landt M., Boltz S. C., Butler L. G. Alkaline phosphatase: affinity chromatography and inhibition by phosphonic acids. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):915–919. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Shackelford D. A., Hurley T. R., Johnson P., Hyman R., Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S. Expression of CD45 alters phosphorylation of the lck-encoded tyrosine protein kinase in murine lymphoma T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8959–8963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen C. J., Sahlin L., Panayotou G., Waterfield M. D. Purification and characterization of placental membrane phosphotyrosine phosphatases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):447–454. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Modulation of protein phosphatases-1 and 2A by histone H1, protamine, polylysine and heparin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roome J., O'Hare T., Pilch P. F., Brautigan D. L. Protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase purified from the particulate fraction of human placenta dephosphorylates insulin and growth-factor receptors. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):493–500. doi: 10.1042/bj2560493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotenberg S. A., Brautigan D. L. Membrane protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase in rabbit kidney. Proteolysis activates the enzyme and generates soluble catalytic fragments. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):747–754. doi: 10.1042/bj2430747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriner C. L., Brautigan D. L. Cytosolic protein phosphotyrosine phosphatases from rabbit kidney. Purification of two distinct enzymes that bind to Zn2+-iminodiacetate agarose. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11383–11390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. W., Brautigan D. L. Specificity of protein phosphotyrosine phosphatases. Comparison with mammalian alkaline phosphatase using polypeptide substrates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2042–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Hall L. R., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that has a cytoplasmic region homologous to the leukocyte common antigen. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1523–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Tsai A. Y., Saito H. A family of receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases in humans and Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8698–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Subrahmanyam G. Purification and characterization of a protein-phosphotyrosine phosphatase from rat spleen which dephosphorylates and inactivates a tyrosine-specific protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7801–7808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom D., Powell A. J., Lloyd C. W., Rees D. A. Rapid isolation of plasma membranes in high yield from cultured fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):187–194. doi: 10.1042/bj1680187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Characterization of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6731–6737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6722–6730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung H. Y., Reed L. J. Identification and purification of a cytosolic phosphotyrosyl protein phosphatase from bovine spleen. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):412–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90469-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Belle H. Kinetics and inhibition of alkaline phosphatases from canine tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 10;289(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Bolen J. B. Post-translational alterations of the tyrosine kinase p56lck in response to activators of protein kinase C. Oncogene Res. 1988 May;2(4):385–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Horak E. M., Bookman M. A., Bolen J. B. Alterations of the lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck) during T-cell activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4353–4361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Goris J., Merlevede W. Purification and properties of polycation-stimulated phosphorylase phosphatases from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1049–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]