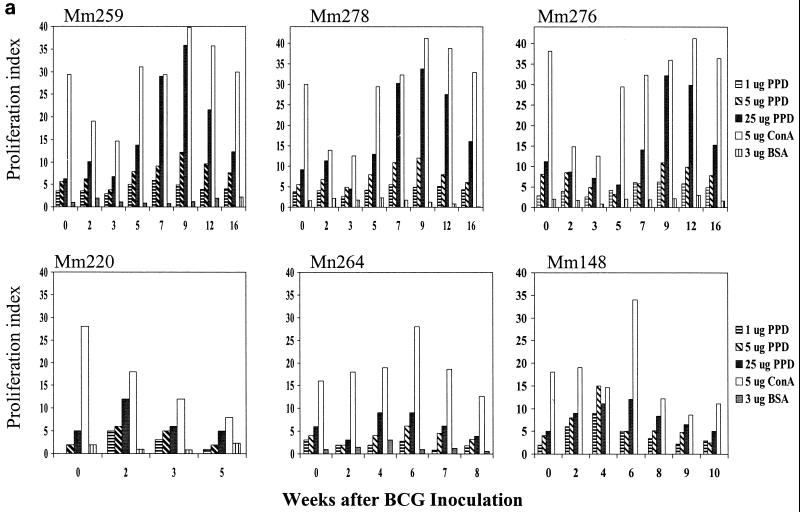
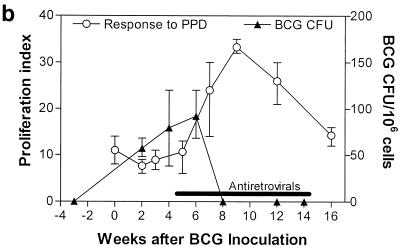
FIG. 3.
Control of fatal SIV-related tuberculosis-like disease in SIV/BCG-coinfected macaques correlated temporally with the restoration of BCG PPD-specific T-cell responses during the period of antiretroviral treatment. The data shown in panel a were generated in proliferation assays, using PBL from the coinfected macaques depleted of CD8+ lymphocytes. (b) Correlation between the resolution of BCG infection and the restored T-cell responses to BCG after antiretroviral treatment. Follow-up studies showed that the ability of T cells to proliferate was suppressed again due to the rebound SIV infection after the discontinuation of antiretroviral treatment (data not shown).