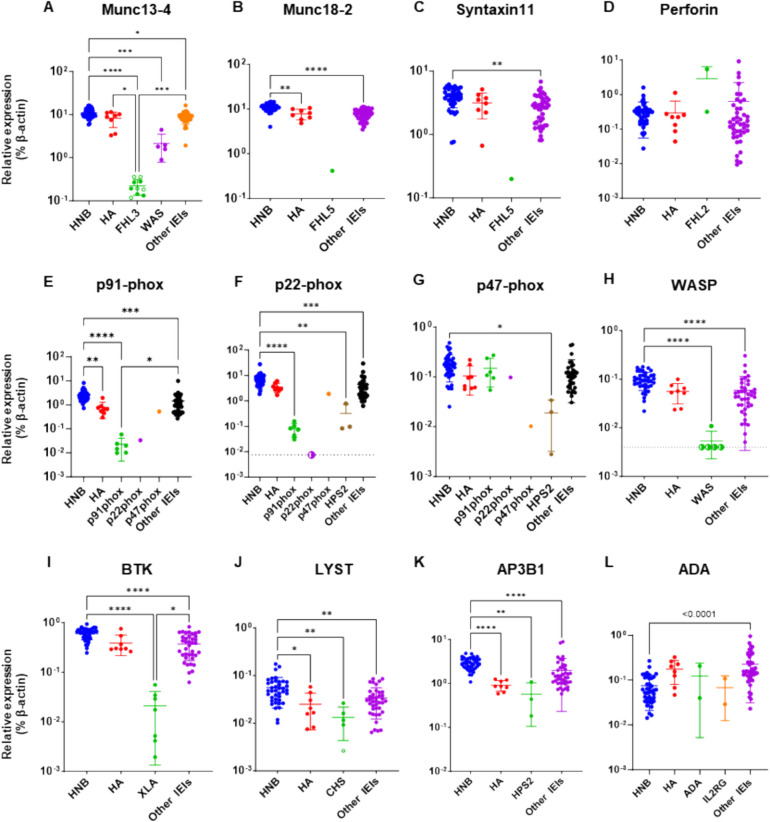
Fig. 4.
Expression of disease-responsible proteins in samples from patients with inborn errors of immunity. Proteomics evaluation of disease-responsible proteins in samples from healthy newborns (HNB), healthy adults (HA), and patients with IEIs, including: familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) type 2, 3, and 5 (FHL2: n = 2, FHL3: n = 8, and FLH5: n = 1, respectively); p91-phox, p22-phox, and p47-phox deficiencies (n = 6, 1, and 1, respectively); Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2 (HPS2: n = 3); Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS: n = 5); X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA: n = 7); Chédiak-Higashi syndrome (CHS: n = 5); adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA: n = 2); common γ chain deficiency (IL2RG: n = 2). All data were standardized relative to the expression of β-actin in the same sample. Levels of (A) Munc13-4, (B) Munc18-2, (C) Syntaxin-11, (D) perforin, (E) p91-phox, (F) p22-phox, (G) p47-phox, (H) WASP, (I) BTK, (J) LYST, (K) AP3B1, and (L) ADA in samples from HNB, HA, and patients with IEIs. Open symbols, samples obtained from pre-symptomatic newborn patients with IEIs; half-closed symbols, results under the limit of detection plotted at approximate lower detection limits. Statistical differences among groups were analyzed using one-way ANOVA on ranks (the Kruskal–Wallis test), followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons. Data represent the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001