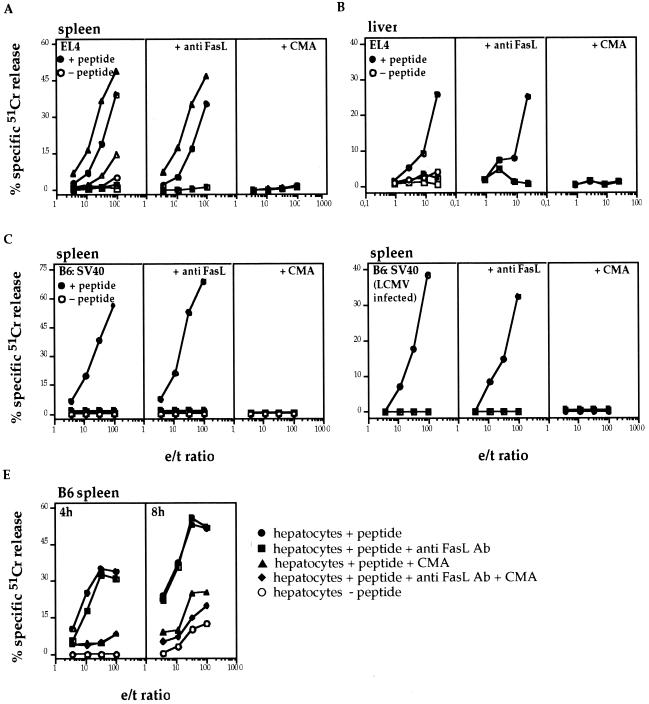
FIG. 5.
In vitro cytolytic activity of LCMV-immune cells. B6 (circles; A to E), gld (triangles; A), and perf×gzmA×B−/− (squares; A to D) were infected i.p. with 105 PFU of LCMV. Primary LCMV-immune cells (B6, gld, and perf×gzmA×B−/−) were collected from the spleen and/or the liver on d 8 p.i. and then tested for their cytolytic activity. (A) Primary LCMV-immune cells from the spleen of B6, gld, and perf×gzmA×B−/− mice were tested on EL4 target cells with (solid symbols) or without (open symbols) previous incubation of the EL4 target cell with LCMV-specific peptide. Aliquots of effector cells were exposed to anti-FasL antibody (30 min) or, alternatively, CMA (2 h) to test which cytotoxic pathways are involved in the killing process. (B) Same as panel A, except that primary LCMV-immune cells from the liver of B6 and perf×gzmA×B−/− mice were used. (C) Same as panel A for B6 and perf×gzmA×B−/−, except that the target cells were B6:SV40. (D) Primary LCMV-immune cells from the spleen of B6 and perf×gzmA×B−/− mice were tested on LCMV-infected B6:SV40 target cells (24 h) alone or in the presence of anti-FasL antibody or CMA. (E) Primary LCMV-immune cells from the spleen of B6 mice were tested on ex vivo hepatocytes in the presence (●) or absence (○) of LCMV-specific peptide. The cytolytic activities were tested after 4 and 8 h. Aliquots of effector cells were exposed to anti-FasL antibody (■) or, alternatively, CMA (▴). Finally, effector cells were incubated with anti-FasL antibody and CMA together (⧫).