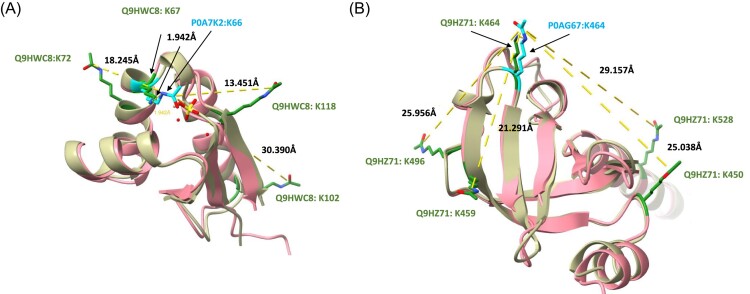
Figure 2.
Lysine acetylation of the ribosomal proteins, Q9HWC8 and Q9HZ71, in P. aeruginosa surrounding two sites that were shown to have potential regulatory role - via mutational studies — in E. coli by Zhang et al. (2020). In this figure, acetylation sites that were measured in this study are highlighted in green on the Pseudomonas AlphaFold structures (Jumper et al. 2021, Varadi et al. 2022) (beige) using ChimeraX (Goddard et al. 2018, Pettersen et al. 2021, Meng et al. 2023). Two sites described by Zhang et al. (2020), K66 in protein P0A7K2 and K464 in protein P0AG67, are highlighted in cyan on the E. coli structures (pink). The P0A7K2 structure originates from the PDB database (1CTF) (Leijonmarck and Liljas 1987, Berman et al. 2000) and P0AG67 from the AlphaFold database (Varadi et al. 2022). Seven of the measured acetylation sites are located relatively closely to these previously characterised sites, thereby suggesting a possible regulatory role of these sites as well.