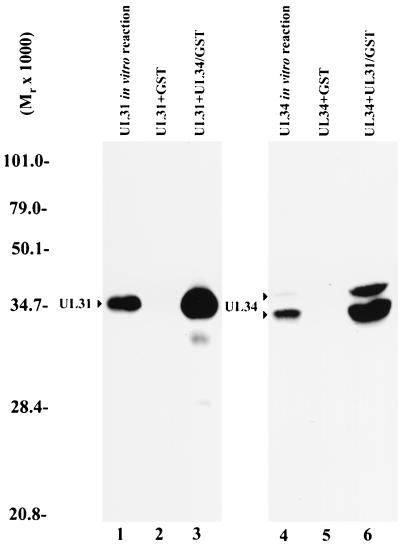
FIG. 6.
Digitized fluorographic image of GST pull-down reactions using equal amounts of GST or GST fusion proteins reacted with either in vitro-expressed radiolabeled UL31 protein (left panel) or radiolabeled UL34 protein (right panel). GST pull-down reactions in lanes 2, 3, 5, and 6 were performed similarly. Radiolabeled protein was added to Sepharose beads bearing either GST or GST fused to the putative interaction partner. After incubation, the beads were washed extensively, followed by elution in SDS sample buffer and electrophoretic separation on a denaturing polyacrylmide gel. The gel was subjected to analysis on a Molecular Dynamics PhosphorImager and fluorography. Lane 1, product of UL31 transcribed and translated in vitro. The amount of radiolabeled UL31 protein loaded in lane 1 was approximately 20% of that used in the reactions shown in lanes 2 and 3. Lane 2, radiolabeled UL31 protein bound to GST immobolized on Sepharose beads. Lane 3, radiolabeled UL31 protein bound to Sepharose beads containing UL34-GST. Lane 4, radiolabeled UL34 protein produced in an in vitro transcription-translation reaction. The amount of UL34 protein loaded in lane 4 was approximately 20% of that used in reactions shown in lanes 5 and 6. Lane 5, radiolabeled UL34 protein bound to immobilized GST. Lane 6, radiolabeled UL34 protein bound to immobilized UL31-GST. Molecular weights are indicated in thousands to the left of the figure.