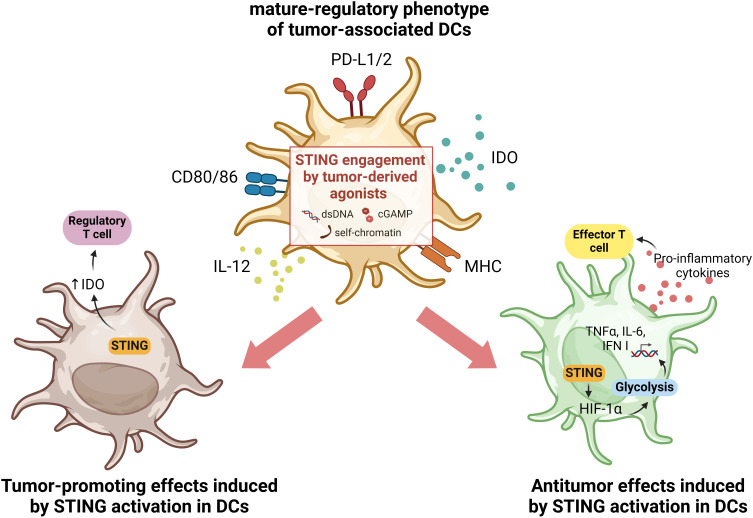
Figure 1.
Illustration of the dual effects of STING activation in tumor-associated DCs. Tumor-associated DCs often display a mature-regulatory phenotype, characterized by the upregulation of both co-stimulatory as well as co-inhibitory molecules. In this context, it has been reported that the activation of STING in tumor-associated DCs may also play a dual role. On the one hand, engagement of the STING receptor can sustain antitumor effects by inducing HIF-1α, which supports glycolysis in DCs, associated with an active and mature phenotype of these cells. This induces an IFN I-mediated response with secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines that trigger effector T cell responses fighting the tumor (right panel). Conversely, activation of the STING pathway has also been reported to support pro-tumorigenesis, by inducing regulation of IDO expression and consequently enhancing regulatory T cell polarization (left panel). Created with BioRender.com.