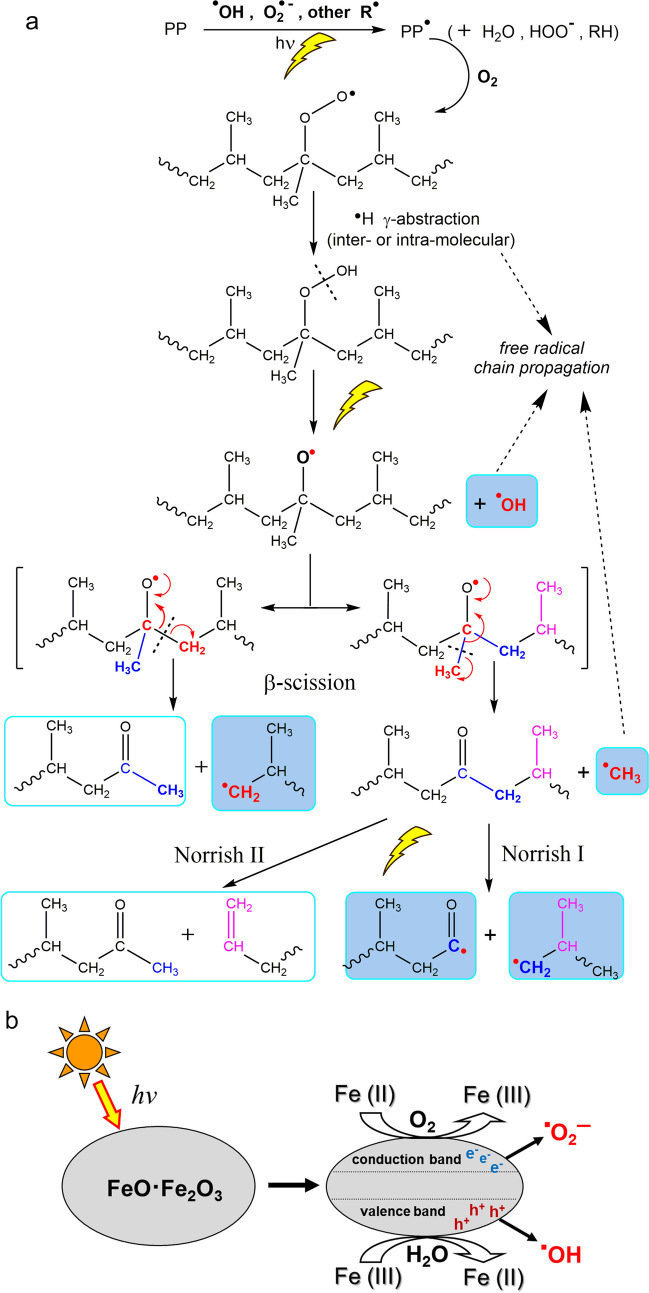
Fig. 1.
A PP photo-oxidative degradation pathways: H-abstraction (more likely on tertiary carbons), followed by oxygen pickup and further H-abstraction by the new peroxy-radical; the resulting thermo- and photo-labile hydroperoxide decomposes into oxy-radical, and eventually ketones upon various β-scissions mechanisms involving the main chain C–C bond; Norrish type reactions of ketones cause further main chain scissions, all the above generating new free radicals (highlighted in the figure), with cascade amplification of the degradation reactions. B Schematized photo-activated generation of ROS by hole (h+) or electron (e−) transfer from magnetite