Abstract
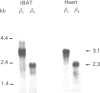
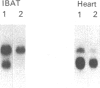
The aim of the present work was to study the effect of hypothyroidism on the expression of the beta-adrenergic receptor (beta-AR) in interscapular brown adipose tissue and heart. The total density of plasma membrane beta-AR per tissue is decreased by 44% in hypothyroid rat interscapular brown adipose tissue and by 55% in hypothyroid rat heart compared with euthyroid controls. The effects of hypothyroidism on the density of both beta 1- and beta 2-AR subtypes were also determined in competition displacement experiments. The densities of beta 1- and beta 2-AR per tissue are decreased by 50% and 48% respectively in interscapular brown adipose tissue and by 52% and 54% in the heart. Northern blot analysis of poly(A)+ RNA from hypothyroid rat interscapular brown adipose tissue demonstrated that the levels of beta 1- and beta 2-AR mRNA per tissue are decreased by 73% and 58% respectively, whereas in hypothyroid heart, only the beta 1-AR mRNA is decreased, by 43%. The effect of hypothyroidism on the beta 1-AR mRNA is significantly more marked in the interscapular brown adipose tissue than in the heart. These results indicate that beta-AR mRNA levels are differentially regulated in rat interscapular brown adipose tissue and heart, and suggest that the decrease in beta-AR number in interscapular brown adipose tissue and heart of hypothyroid animals may in part be explained by a decreased steady-state level of beta-AR mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrass I. B., Scarpace P. J. Glucocorticoid regulation of myocardial beta-adrenergic receptors. Endocrinology. 1981 Mar;108(3):977–980. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-3-977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. P., Kung L. S. beta-Adrenergic receptors in rat heart: effects of thyroidectomy. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 May 15;43(2):207–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L., Folléa N., Paradis A., Collet A. Stereospecific stimulation of brown adipocyte respiration by catecholamines via beta 1-adrenoreceptors. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):E552–E563. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.6.E552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. Y., Kunos G. Short term effects of triiodothyronine on rat heart adrenoceptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):313–320. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung F. Z., Lentes K. U., Gocayne J., Fitzgerald M., Robinson D., Kerlavage A. R., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human brain beta-adrenergic receptor. Evolutionary relationship to rodent and avian beta-receptors and porcine muscarinic receptors. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):200–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Marinetti G. V. Hormone action at the membrane level. VIII. Adrenergic receptors in rat heart and adipocytes and their modulation by thyroxine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 3;541(3):334–346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T., Marinetti G. V. Thyroxine and propylthiouracil effects of vivo on alpha and beta adrenergic receptors in rat heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):984–991. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91615-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Bouvier M., Bolanowski M. A., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cAMP stimulates transcription of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene in response to short-term agonist exposure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors in hamster smooth muscle cells are transcriptionally regulated by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9067–9070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Quarmby V. E., French F. S., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Regulation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor and its mRNA in the rat ventral prostate by testosterone. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jun 6;233(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Delavier-Klutchko C., Kaveri S. V., Durieu-Trautmann O., Strosberg A. D. Structure of the gene for human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: expression and promoter characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6995–6999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. O., Frydman M. L. Nonshivering thermogenesis in the rat. II. Measurements of blood flow with microspheres point to brown adipose tissue as the dominant site of the calorigenesis induced by noradrenaline. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;56(1):110–122. doi: 10.1139/y78-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freake H. C., Oppenheimer J. H. Stimulation of S14 mRNA and lipogenesis in brown fat by hypothyroidism, cold exposure, and cafeteria feeding: evidence supporting a general role for S14 in lipogenesis and lipogenesis in the maintenance of thermogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3070–3074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frielle T., Collins S., Daniel K. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning of the cDNA for the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7920–7924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacobino J. P. Subcellular fractionation of brown adipose tissue. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(4):445–449. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocayne J., Robinson D. A., FitzGerald M. G., Chung F. Z., Kerlavage A. R., Lentes K. U., Lai J., Wang C. D., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Primary structure of rat cardiac beta-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors obtained by automated DNA sequence analysis: further evidence for a multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8296–8300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest S. J., Hadcock J. R., Watkins D. C., Malbon C. C. Beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor expression in differentiating 3T3-L1 cells. Independent regulation at the level of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5370–5375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors: agonist-induced reduction in receptor mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by "permissive" hormones: glucocorticoids increase steady-state levels of receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8415–8419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Ros M., Malbon C. C. Agonist regulation of beta-adrenergic receptor mRNA. Analysis in S49 mouse lymphoma mutants. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13956–13961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himms-Hagen J. Brown adipose tissue metabolism and thermogenesis. Annu Rev Nutr. 1985;5:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.05.070185.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodin R. A., Lazar M. A., Wintman B. I., Darling D. S., Koenig R. J., Larsen P. R., Moore D. D., Chin W. W. Identification of a thyroid hormone receptor that is pituitary-specific. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2539642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg L., Axelrod J. Influence of pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal hormones on norepinephrine turnover and metabolism in the rat heart. Circ Res. 1968 May;22(5):559–571. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.5.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. E., Sullivan A. C. Beta-1 receptor is the predominant beta-adrenoreceptor on rat brown adipose tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):681–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurchie E. J., Patten G. S., Charnock J. S., McLennan P. L. The interaction of dietary fatty acid and cholesterol on catecholamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in the rat heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 9;898(2):137–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Hegstrand L. R., Molinoff P. B. Simultaneous determination of beta-1 and beta-2-adrenergic receptors in tissues containing both receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):34–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi A., Whitsett J. A. Ontogeny of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in the rat myocardium: effects of hypothyroidism. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 17;86(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90394-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Kawaichi M., Brownstein M., Lee F., Yokota T., Arai K. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA; construction and screening of cDNA expression libraries for mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:3–28. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON R. E. The influence of the thyroid on adrenal cortical function. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):736–743. doi: 10.1172/JCI103659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J. A role for brown adipose tissue in diet-induced thermogenesis. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):31–35. doi: 10.1038/281031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J., Sudera D. K. Beta-adrenoreceptors in rat brown adipose tissue: proportions of beta 1- and beta 2-subtypes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 1):E397–E402. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.4.E397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Forman B. M., Horowitz Z. D., Ye Z. S. Regulation of gene expression by thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):957–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI113449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpace P. J., Baresi L. A., Morley J. E. Glucocorticoids modulate beta-adrenoceptor subtypes and adenylate cyclase in brown fat. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 1):E153–E158. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.2.E153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seydoux J., Giacobino J. P., Girardier L. Impaired metabolic response to nerve stimulation in brown adipose tissue of hypothyroid rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Feb;25(2):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seydoux J., Girardier L. Control of brown fat thermogenesis by the sympathetic nervous system. Experientia Suppl. 1978;32:153–167. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-5559-4_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triandafillou J., Gwilliam C., Himms-Hagen J. Role of thyroid hormone in cold-induced changes in rat brown adipose tissue mitochondria. Can J Biochem. 1982 May;60(5):530–537. doi: 10.1139/o82-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Pollinger J., Matz S. beta-Adrenergic receptors and catecholamine sensitive adenylate cyclase in developing rat ventricular myocardium: effect of thyroid status. Pediatr Res. 1982 Jun;16(6):463–469. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198206000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight P. A., Crew M. D., Spindler S. R. Discrete positive and negative thyroid hormone-responsive transcription regulatory elements of the rat growth hormone gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5659–5663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Lefkowitz R. J., Watanabe A. M., Hathaway D. R., Besch H. R., Jr Thyroid hormone regulation of beta-adrenergic receptor number. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2787–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zähringer J., Klaubert A. The effect of triiodothyronine on the cardiac mRNA. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1982 Oct;14(10):559–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(82)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]