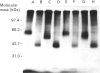
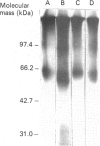
Abstract
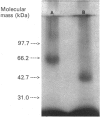
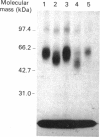
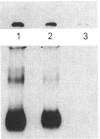
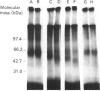
We used inhibitors of four steps of the glycosylation pathway to examine the contribution of carbohydrate moieties to the ligand-binding activity, cell-surface expression and apparent molecular mass of the human vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptor. Human melanoma IGR 39 cells, incubated for 60 h with the inhibitors tunicamycin, castanospermine, swainsonine or deoxymannojirimycin, under conditions where cell viability and protein synthesis were not affected, expressed VIP receptor species with different VIP-binding properties. The most pronounced effects on VIP binding were obtained with tunicamycin and deoxymannojirimycin, which respectively caused 80% and 67% inhibition. Treatment with either swainsonine or castanospermine resulted in only a 25-32% decrease in VIP specific binding. Based on Scatchard analyses of data from competition experiments, the decrease in VIP-binding activity in either swainsonine- or deoxymannojirimycin-treated cells was due to a decrease in ligand affinity; the cell-surface number of VIP-binding sites remained unchanged. In contrast, tunicamycin and castanospermine caused decreases in the cell-surface number of functional VIP receptors without affecting affinity. Besides, the drug-treated cells produced VIP-binding proteins with different molecular masses and endoglycosidase H (Endo H) sensitivities. When compared with their counterpart synthesized in control cells, VIP-binding proteins produced by deoxymannojirimycin- or swainsonine-treated cells were smaller in size and exhibited the expected sensitivity to Endo H. No modification in the apparent molecular mass was observed in the presence of either castanospermine or tunicamycin. In addition, after Endo F digestion, all of the deglycosylated proteins migrated with the same electrophoretic mobility. Finally, processing in the presence of castanospermine led to an Endo H-resistant receptor species which showed an unexpected neuraminidase-sensitivity, indicating that, as in control cells, these receptors carry V-linked oligosaccharides with terminal sialic acid residues.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Yamada K. M. Analysis of the role of glycosylation of the human fibronectin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18011–18018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert C., Rougé F., Galindo J. R. Tumorigenicity of human malignant melanocytes in nude mice in relation to their differentiation in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 May;64(5):1029–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boege F., Ward M., Jürss R., Hekman M., Helmreich E. J. Role of glycosylation for beta 2-adrenoceptor function in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9040–9049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Matlin K., Bause E., Legler G., Peyrieras N., Ploegh H. Inhibition of N-linked oligosaccharide trimming does not interfere with surface expression of certain integral membrane proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):551–556. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01845.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvineau A., Voisin T., Guijarro L., Laburthe M. Purification of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor from porcine liver by a newly designed one-step affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13386–13390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foddy L., Hughes R. C. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides in baby hamster kidney cells treated with castanospermine, an inhibitor of processing glucosidases. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):291–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Legler G., Ploegh H. Novel mannosidase inhibitor blocking conversion of high mannose to complex oligosaccharides. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):755–758. doi: 10.1038/307755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Ruoho A. E., Malbon C. C. N-glycosylation in expression and function of beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16559–16564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross V., Tran-Thi T. A., Schwarz R. T., Elbein A. D., Decker K., Heinrich P. C. Different effects of the glucosidase inhibitors 1-deoxynojirimycin, N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin and castanospermine on the glycosylation of rat alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):853–860. doi: 10.1042/bj2360853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvie K. R., Niznik H. B., Seeman P. Dopamine D2 receptor binding subunits of Mr congruent to 140,000 and 94,000 in brain: deglycosylation yields a common unit of Mr congruent to 44,000. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;34(2):91–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz K. N., Lohse M. J. The glycoprotein nature of A1 adenosine receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):406–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubas W. A., Spiro R. G. Evaluation of the role of rat liver Golgi endo-alpha-D-mannosidase in processing N-linked oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3990–3998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubas W. A., Spiro R. G. Golgi endo-alpha-D-mannosidase from rat liver, a novel N-linked carbohydrate unit processing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3775–3781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luis J., Martin J. M., el Battari A., Marvaldi J., Pichon J. The vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptor: recent data and hypothesis. Biochimie. 1988 Oct;70(10):1311–1322. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luis J., Martin J. M., el Battari A., Reynier M., Marvaldi J., Pichon J. A human melanoma-derived cell line (IGR39) with a very high number of vasoactive-intestinal-peptide (VIP) receptors. 1. Molecular characterization of the binding site. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):429–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchis-Mouren G., Martin J. M., Luis J., el Battari A., Muller J. M., Marvaldi J., Pichon J. HT 29, a model cell line: stimulation by the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP); VIP receptor structure and metabolism. Biochimie. 1988 May;70(5):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. M., Darbon H., Luis J., el Battari A., Marvaldi J., Pichon J. Photoaffinity labelling of the vasoactive-intestinal-peptide-binding site on intact human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line HT29-D4. Synthesis and use of photosensitive vasoactive-intestinal-peptide derivatives. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):679–685. doi: 10.1042/bj2500679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. M., Luis J., Marvaldi J., Pichon J., Pic P. A human melanoma-derived cell line (IGR39) with a very high number of vasoactive-intestinal-peptide (VIP) receptors. 2. Effect of VIP on cAMP production and on cell-surface VIP-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):435–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Smith M. M. Synthesis and assembly of acetylcholine receptor, a multisubunit membrane glycoprotein. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01870209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. E., Spiro R. G. Demonstration that Golgi endo-alpha-D-mannosidase provides a glucosidase-independent pathway for the formation of complex N-linked oligosaccharides of glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13104–13112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T. D., Williams J. A., Gray G. M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor on liver plasma membranes: characterization as a glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):361–368. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson T. S., Bamberger M. J., Lane M. D. Post-translational changes in tertiary and quaternary structure of the insulin proreceptor. Correlation with acquisition of function. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7342–7351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson T. S., Lane M. D. A common mechanism for posttranslational activation of plasma membrane receptors? FASEB J. 1989 Mar;3(5):1618–1624. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.5.2537774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palamarczyk G., Elbein A. D. The effect of castanospermine on the oligosaccharide structures of glycoproteins from lymphoma cell lines. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):795–804. doi: 10.1042/bj2270795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y. T., Hori H., Saul R., Sanford B. A., Molyneux R. J., Elbein A. D. Castanospermine inhibits the processing of the oligosaccharide portion of the influenza viral hemagglutinin. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3975–3984. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives J., Bar-Sagi D. Effect of tunicamycin, an inhibitor of protein glycosylation, on the biological properties of acetylcholine receptor in cultured muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1775–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP): current status. Peptides. 1984 Mar-Apr;5(2):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunier B., Kilker R. D., Jr, Tkacz J. S., Quaroni A., Herscovics A. Inhibition of N-linked complex oligosaccharide formation by 1-deoxynojirimycin, an inhibitor of processing glucosidases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14155–14161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slieker L. J., Martensen T. M., Lane M. D. Synthesis of epidermal growth factor receptor in human A431 cells. Glycosylation-dependent acquisition of ligand binding activity occurs post-translationally in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15233–15241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. Deglycosylated mammalian beta 2-adrenergic receptors: effect on radioligand binding and peptide mapping. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Feb 15;237(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M., De Neef P., Tastenoy M., Christophe J. Molecular characteristics and evidence for internalization of vasoactive-intestinal-peptide (VIP) receptors in the tumoral rat-pancreatic acinar cell line AR 4-2 J. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):707–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Lampen O. Tunicamycin inhibition of polyisoprenyl N-acetylglucosaminyl pyrophosphate formation in calf-liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Touster O. Swainsonine causes the production of hybrid glycoproteins by human skin fibroblasts and rat liver Golgi preparations. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7578–7585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagishita M. Tunicamycin inhibits proteoglycan synthesis in rat ovarian granulosa cells in culture. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Nov 15;251(1):287–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Battari A., Luis J., Martin J. M., Fantini J., Muller J. M., Marvaldi J., Pichon J. The vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor on intact human colonic adenocarcinoma cells (HT29-D4). Evidence for its glycoprotein nature. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):185–191. doi: 10.1042/bj2420185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]