Figure 3.
Drosophila dSgip1 localizes to synapses and the pathogenic mutant lowers protein stability
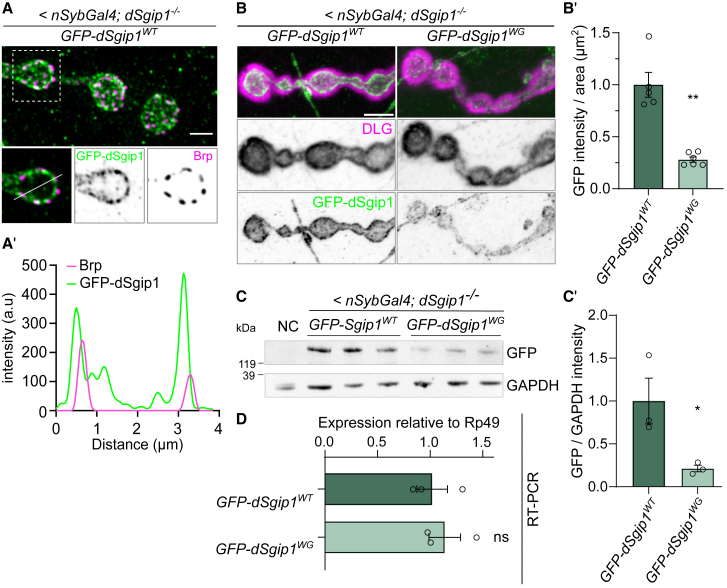
(A) Maximum projection composite Airyscan confocal image of an NMJ expressing GFP-dSgip1WT (<nSybGal4; dSgip1−/−) and labeled with anti-GFP (green) and anti-Brp (nc82, magenta) antibodies, where Brp marks active zones. Insert: a single confocal section. Scale bar: 2 μm. (A′) Fluorescence intensity plot (arbitrary units) along the line indicated in insert in (A).
(B) Representative maximum projection composite confocal images of NMJs of flies expressing wild-type or mutant GFP-dSgip1 (GFP-dSgip1WT or W694G) (<nSybGal4; dSgip1−/−) and stained with anti-GFP (green) and anti-DLG antibodies (magenta), where DLG marks the post-synaptic site. Scale bar: 5 μm.
(B′) Quantification of the average GFP intensity per NMJ area. 4 NMJs per animal were analyzed, n ≥ 5 animals per genotype. Statistical significance: unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. ∗∗p < 0.01. Bars: mean ± SEM.
(C and C′) Western blot from adult Drosophila head lysates of indicated genotypes labeled with anti-GFP marking GFP-dSgip1 and anti-GAPDH (loading control) (C) and the quantification of GFP-dSgip1 protein levels (C′). Values are relative to GAPDH for the three replicates of each genotype. NC (negative control): flies not expressing any GFP construct. Statistical significance: unpaired t test. ∗p < 0.05. Bars: mean ± SEM; points are individual values and n ≥ 3 per genotype.
(D) Quantitative RT-PCR to assess GFP-dSgip1 expression levels in adult head extracts relative to Rp49. RT-PCR primers were designed against dSgip1. While RNA levels of the W694G variant and wild-type variant are indistinguishable, there is less W694G mutant protein at synapses than wild-type protein (C), indicating the mutations destabilize dSgip1. Statistical significance: unpaired t test. ns, not significant. Bars: mean ± SEM; points are individual values and n ≥ 3.