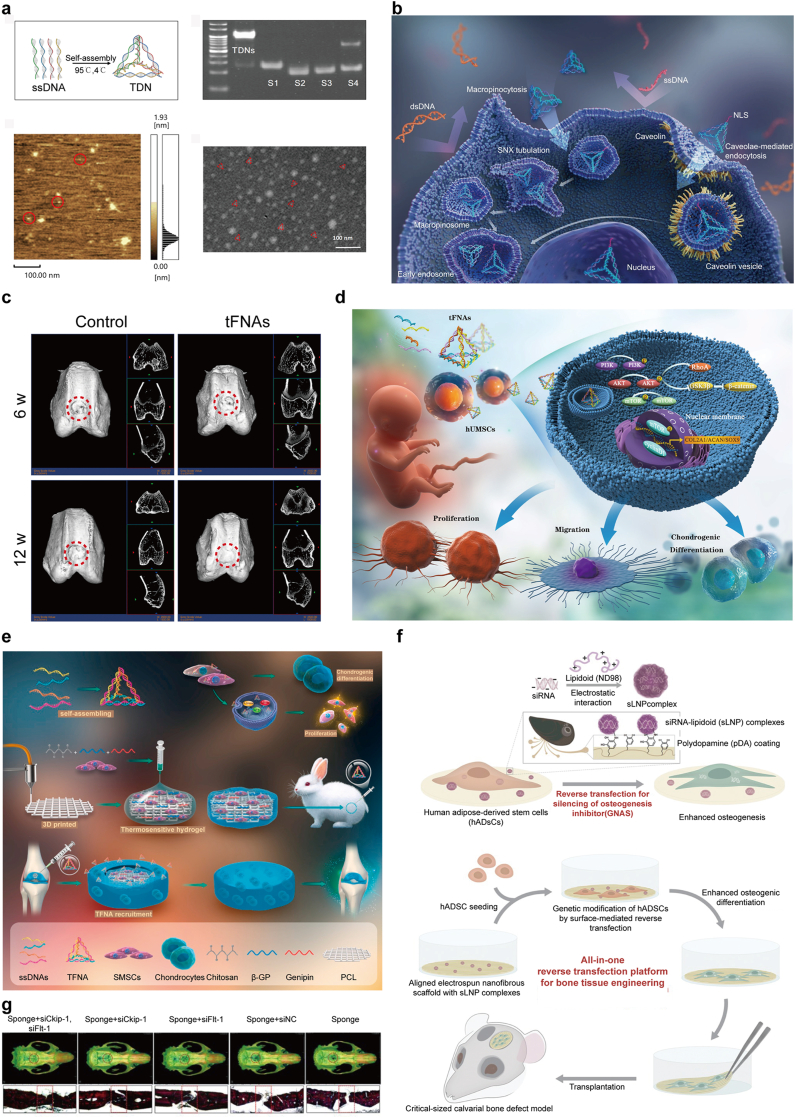
Fig. 5.
a) Characterization of TDNs. Reproduced with permission [72]. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH Verlag. b) tFNAs can enter cells, unlike naked DNA which cannot cross cell membranes. tFNAs with nuclear localization sequences (NLSs) also reach the nucleus, showcasing their targeted delivery potential. Reproduced with permission [53]. Copyright 2022, Springer Nature. c) tFNAs enhance transformation of SMSC into cartilage cells and boost joint cartilage repair in living organisms. Reproduced with permission [61]. Copyright 2021, KeAi Communications Co. d) Bone regeneration in the rat skull defect model. Reproduced with permission [67]. Copyright 2014, Dove Medical Press Ltd. e) TFNA boosts SMSC growth and aids their transformation into cartilage cells. Combined with a CS hydrogel and 3D-printed polycaprolactone (PCL) scaffold, it effectively repairs rabbit cartilage defects. Reproduced with permission [75]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier BV. f) pDA helps attach sLNP complexes to PLGA scaffolds for efficient siRNA delivery, boosting bone formation from ADSCs. This method offers a unified solution for stem cell engineering, differentiation and implantation, effectively repairing large bone defects in mice. Reproduced with permission [66]. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH Verlag.