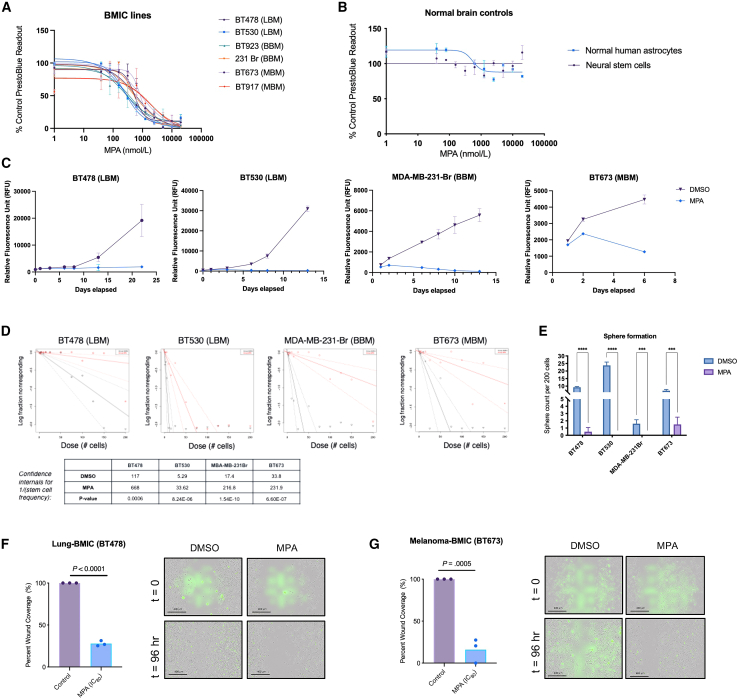
Figure 2.
MPA is a selective anti-BMIC inhibitor
(A) Dose-response curves of multiple lung-BM (LBM), breast-BM (BBM), and melanoma-BM (MBM) cells, and (B) control normal brain cells after a 72-h treatment with MPA. PrestoBlue readout is normalized to vehicle-treated cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD from 4 technical replicates.
(C) Assessment of cell viability of patient-derived BMICs treated with MPA or its vehicle. PrestoBlue readout is normalized to vehicle-treated cells, p < 0.0001.
(D) Limiting dilution analysis regression curves of patient-derived BMICs after a 6-day treatment with MPA or its vehicle: plotted using the extreme limiting dilution program (available from: http://bioinf.wehi.au/software/elda/).
(E) Quantification of tumor spheres formed by patient-derived BMICs after 72-h treatment with MPA or its vehicle. Sphere count normalized to vehicle-treated cells, p < 0.0001.
(F and G) Percent wound closure of DMSO control vs. MPA-treated cells expressed as an average of replicates (n = 3) and images are taken at 10× magnification. Wound closure (represented by dotted white line) is measured using ImageJ on Incucyte-derived images, p values are indicated. Scale bars are 400 μm. See also Videos S1, S2, S3, and S4. Comparisons of cell viability, sphere formation, and wound closure were made via a two-tailed unpaired t test and data are presented as mean ± SD from 3 to 4 technical replicates. SYTOX green nucleic acid stain indicates cell death.