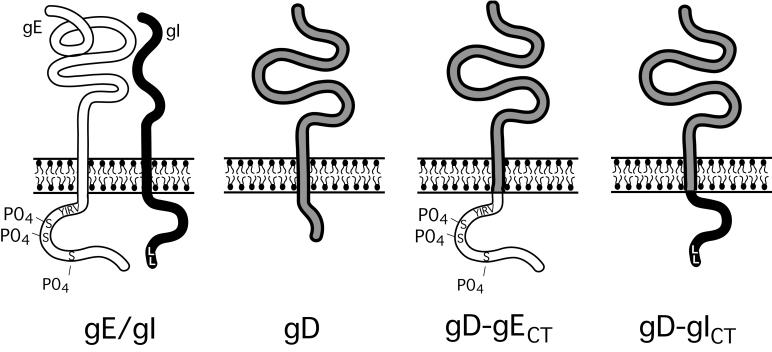
FIG. 1.
Schematic of HSV-1 glycoproteins gE/gI and gD and of glycoproteins chimeric gD-gECT and gD-gICT. The CT domain of gE is 106 residues in length (aa 447 to 552) and contains a tyrosine motif (YIRV), a cluster of acidic residues adjacent to several serine residues that are phosphorylated (58). The CT domain of gI is 94 residues in length (aa 297 to 390) and contains a dileucine motif at the C terminus. The gE and gI CT domains were transferred onto the extracellular and transmembrane domains of gD (residues 1 to 364), replacing the gD CT domain, creating gD-gECT and gD-gICT, respectively.