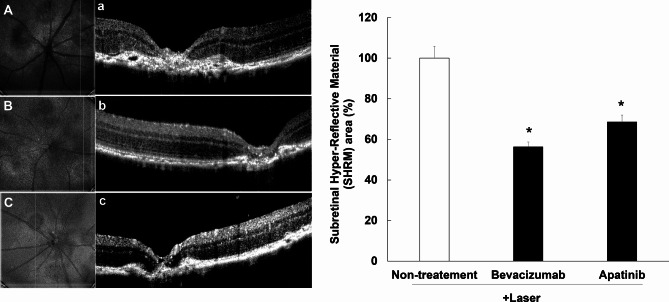
Fig. 7.
Inhibitory effects of apatinib on the expression of hyper-reflective lesions in mice with laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV). Laser photocoagulation spots were identified in digital red-free retinal images (non-treatment: (A) bevacizumab: (B) apatinib: (C). Using the center of the laser spot as reference, retinal OCT scans were performed in the vertical plane (non-treatment: (a) bevacizumab: (b) apatinib: (c). Hyper-reflective lesions were confirmed on OCT images. Thereafter, the inner border of the lesion was manually outlined, whereas the hyper-reflective area (mean area of vertical and horizontal planes) was measured using Image J software (version 1.53, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html). The hyper-reflective lesion area was significantly decreased after intravitreal administration of apatinib (1 µg/1 µL in DMSO) and bevacizumab as positive control (25 µg/1 µL) (D). Data were analyzed using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s test (*p < 0.05 vs. only laser-induced CNV group), and the results are expressed as mean ± S.E. (n = 10–29).