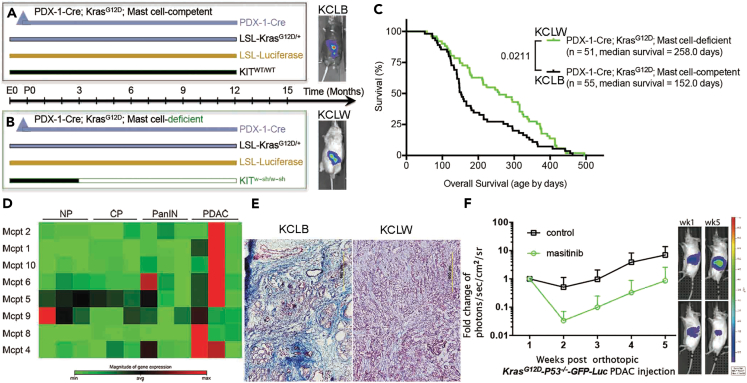
Figure 2.
Depleting mast cells suppressed PDAC growth and improved response to immunotherapy
(A and B) Breeding strategy to develop mast cell-competent and mast cell-deficient mice that spontaneously develop pancreatic cancer. (A) PDX-1Cre; KrasLSL−G12D/+(KC); LSL-Luciferase; Kitwt/wt (KCLB) mast cell-competent. (B) PDX-1Cre; KrasLSL−G12D/+(KC); LSL-Luciferase; KitW-sh/W−sh (KCLW) mast cell-deficient. Mast cell-deficiency was apparent at 3 months of age.
(C) Increased survival of KCLW mast cell-deficient mice compared to mast cell-competent KCLB mice.
(D) cDNA microarray analysis indicated the expression of mast cell proteases were primarily upregulated when the mice developed PDAC in the KPC-GEMM model.
(E) KCLW mast cell-deficient mice presented with less fibrosis in the tumor microenvironment compared to mast cell-competent KCLB mice.
(F) Blocking mast cell function with masitinib inhibited PDAC growth in the authotopic KPC model. Tumor sizes were measured by bioluminescent imaging (BLI-IVIS). Data indicate fold change in photons/sec/cm2/sr ± standard deviation, p = 0.0007 at week 5.