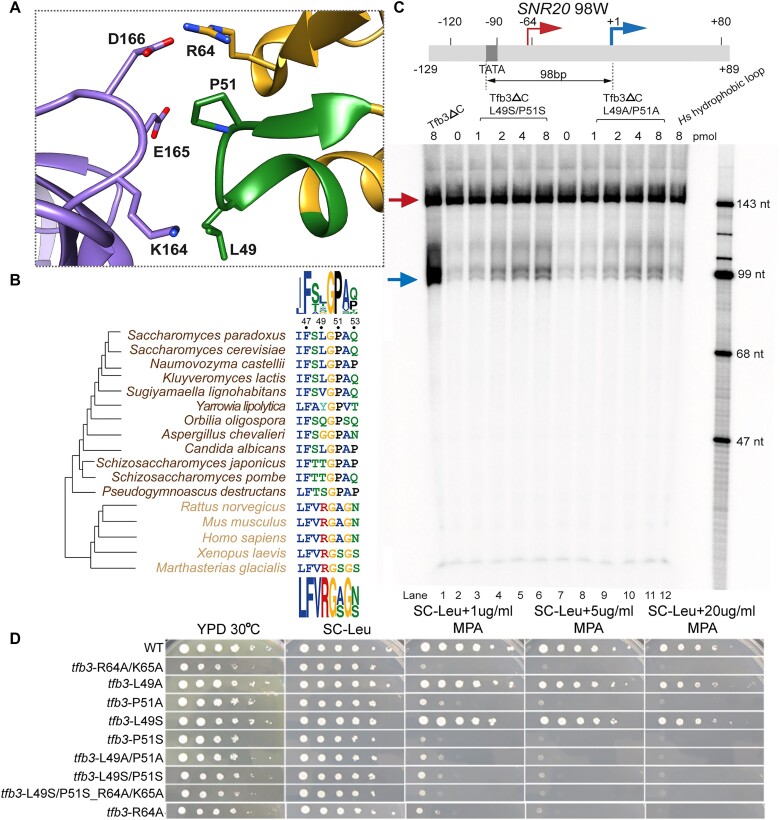
Figure 3.
Pro51 confers distal TSS utilization in S. cerevisiae. (A) Interface between the Tfb3 hydrophobic loop (green) and Rpb7 (purple). (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the hydrophobic loop between fungi (brown) and metazoans (orange). Sequence logos in fungi and metazoans are displayed at the top and the bottom, respectively. (C) Run-off transcription with Tfb3ΔC (lane 1), Tfb3ΔC-L49S/P51S (lanes 2–6), Tfb3ΔC-L49A/P51A (lanes 7–11) and Tfb3ΔC-HsHL (lane 12). Amounts of Tfb3ΔC and mutants added into the reactions are indicated above each lane. The assay was performed with SNR20 98W promoter DNA (–129/+89) as in Figure 2A. Transcripts initiated from upstream and downstream TSSs are indicated by red and blue arrows. (D) Growth phenotypes of tfb3 mutants. Ten-fold serial dilutions of saturated cultures of TFB3 WT and mutant strains plated on different media at 30°C. YPD is rich medium with dextrose as a carbon source. SC-Leu is defined as complete medium lacking leucine. MPA was added to this medium (SC-Leu + MPA) to 1, 5 and 20 μg/ml final concentrations, showing that P51A and P51S are sensitive to this drug, indicative of defects in TSS scanning at the IMD2 gene, which is required for resistance. Pictures used are of day 2 for YPD, day 3 for SC-Leu and day 4 for the plates with varying concentrations of MPA.