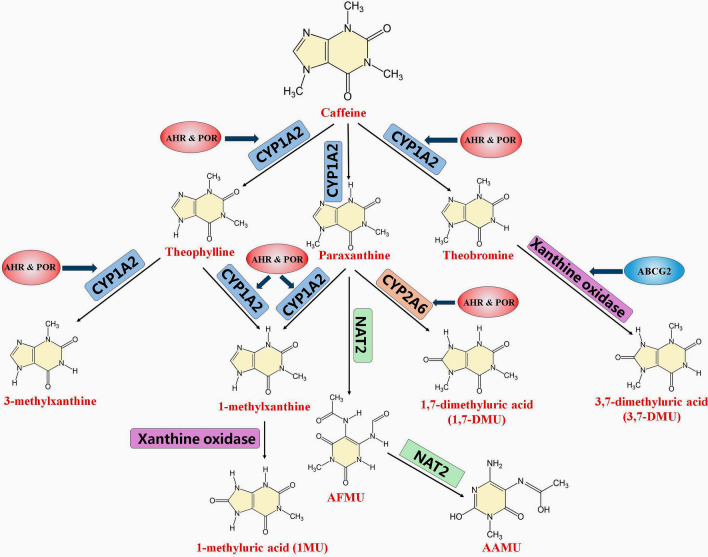
Fig. 2.
Caffeine metabolism pathway and metabolites. Caffeine is primarily metabolized in the liver, undergoing demethylation and oxidation. The main route of caffeine metabolism in humans is via CYP1A2 catalyzed N-3 demethylation to paraxanthine (around 84%), N-1 demethylation to theophylline (around 8%) and N-7 demethylation to theobromine (around 8%). Other than theobromine, paraxanthine, and theophylline, the major metabolites in urine are 3-methylxanthine, 1-methylxanthine, 1-methyl uric acid, 5-acetylamine-6-formylamine-3-methyluracil (AFMU), 5-acetylamino-6-amino-3-methyluracil, 1,7-dimethyl uric acid and 3,7-dimethyl uric acid, which are secondary metabolites of theobromine, paraxanthine, and theophylline catalyzed by CYP1A2, CYP2A6, N-acetyltransferase 2 and xanthine oxidase