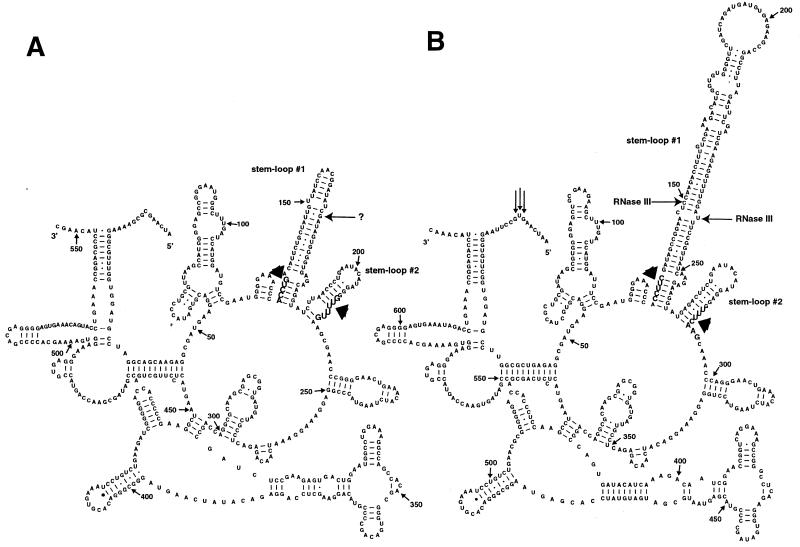
Figure 3.
Structural prediction of RNA segments from the 5′-ends of (A) R.sphaeroides and (B) B.japonicum 23S rRNAs. Shown are 553 and 635 nt from the 5′-ends of R.sphaeroides and B.japonicum 23S rRNAs, respectively, and the 5′- and 3′-ends are marked. Nucleotide positions are indicated numerically with small arrows at 50 base intervals. The 5′-end(s) of the separate 5′ domain determined by primer extension in R.palustris (20) are marked by vertical arrows. Bases indicated with wide arrows in large font and in boldface denote the boundaries of the internally processed segments removed in vivo, as determined by primer extension, S1 mapping and RNA linker ligation-mediated cDNA cloning and sequencing, which includes two stem–loop structures (#1 and #2). In vitro cleavages by E.coli RNase III on the B.japonicum 23S rRNA precursor are shown by bold horizontal arrows on both sides of stem–loop structure #1 in (B). The in vitro RNase III cleavage detected on the right side of stem–loop structure #1 is also the first detectable intermediate in processing of USDA 4362 and USDA 4377 rRNAs. In vivo cleavage by an unspecified nuclease in the R.sphaeroides 5′ IVS is indicated by an arrow (?) on the right side of stem–loop structure #1 in (A). The model used is described previously (2).