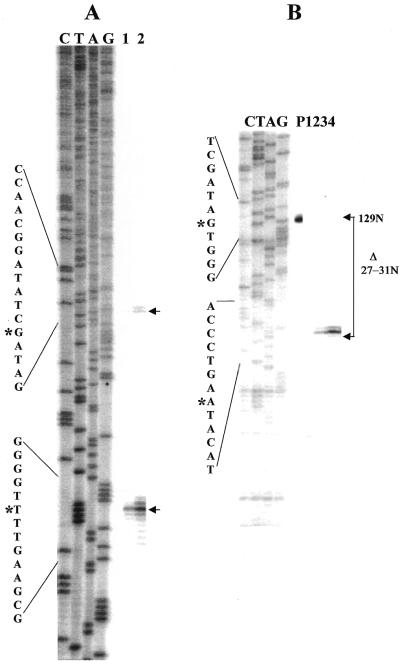
Figure 6.
Defining the limits of the internally processed segment in R.sphaeroides. (A) Primer extension identifies 5′-end of the main segment of R.sphaeroides 23S rRNA and also the location of a processing site in the IVS. Primer extension analysis of total RNA from R.sphaeroides using a 5′-32P-labeled primer at 23S rRNA positions 305–325 complementary to the R.palustris 23S rRNA sequence. Lefthand marker lanes (C, T, A, G) are as described above except R.sphaeroides rDNA was used as template for synthesis. In lanes 1 and 2, 0.5 and 1.5 µg of total RNA were used as template for cDNA synthesis. DNA sequence around the processing sites is presented on the left margin, with position of the cleavage which generates the first detectable intermediate marked by asterisks on the upper sequence and the predominant cleavage which generates completely processed 23S rRNA by an asterisk on the lower sequence. (B) S1 mapping of the 3′-end of the small 5′ 23S rRNA domain. S1 cleavage products are aligned with the same sequence marker as in (A) which is used here only as a size standard. Position of the full-length probe within the sequence is shown by an asterisk in the upper portion of the sequence on the left margin and the position of the most abundant S1 cleavage product by an asterisk on the lower sequence. Brackets on the right margin show the change in size of probe due to S1 cleavage (Δ27–31 nt). Lanes are P, undigested probe; 1, no RNA added; 2, 0.25 µg purified 5′ domain added; 3, 0.5 µg purified 5′ domain added; 4, 1.0 µg purified 5′ domain added.