Figure 7.
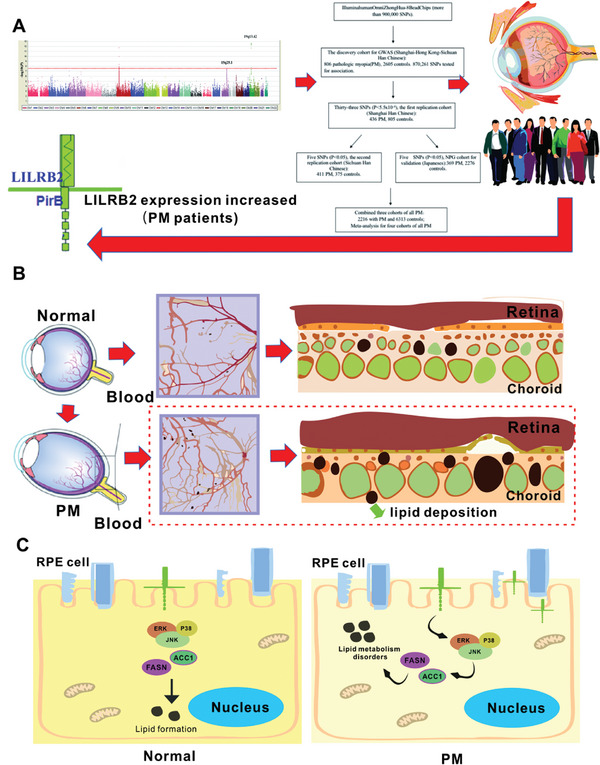
Potential pathogenic mechanisms of LILRB2. A) We identified LILRB2 could be an important candidate gene for PM. B) LILRB2 increases fatty acid synthesis and lipid accumulation in RPE/choroid in different mouse models. C) In cell lines, the lipid accumulation due to overexpression of LILRB2 could be mediated via the activation of ERK1/JNK/P38 signaling, resulting in choroid caverns and worse visual acuity, destroying the function of the choroid and promoting the development of PM.
