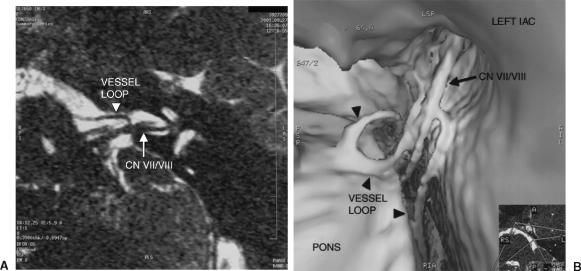
Figure 5.
(A) Oblique axial reformat of CISS data shows a vessel loop, a branch of the anterior inferior cerebellar artery, near CNs VII and VIII at the porus acusticus. (B) Surface model of the left IAC shows the prominent vessel loop in contact with CNs VII and VIII. Vessel loops at this location or at the root entry zone on the brain stem can cause hemifacial spasm. CISS, constructive interference in the steady state; CNs, cranial nerves; IAC, internal auditory canal.