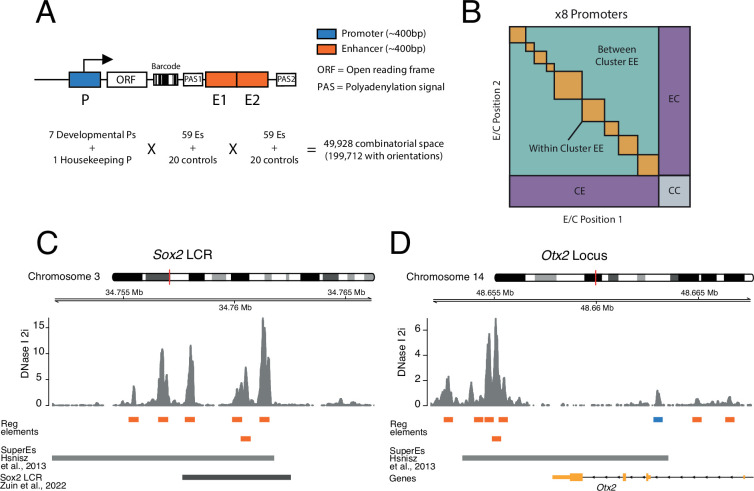
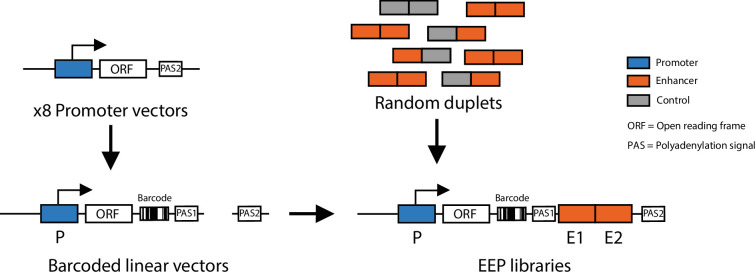
Figure 1. Schematic of three-way combinatorial approach.
(A) Three-way combinatorial massively parallel reporter assay (MPRA) design to test enhancer-enhancer-promoter combinations. Eight barcoded reporter assay libraries, one per promoter, were constructed. Pairs of DNA elements (enhancers and scrambled control sequences) were inserted after barcoded reporter. The enhancers and controls can be placed in both orientations in either the enhancer position 1 (E1) or enhancer position 2 (E2). (B) The design of the library yields eight matrices that contain control-control combinations (CC), enhancer-control combinations (EC and CE), and enhancer-enhancer combinations (EE). (C and D) Two example loci, Sox2 LCR (locus control region) (C) and Otx2 (D) from where we selected enhancers to test in the reporter libraries. Enhancers (orange) were defined around DNAse I hypersensitivty sites from mouse embryonic stem cells (mESC). Promoters (blue) were chosen according to transcription start site (TSS) annotation and mESC DNAse I hypersensitivty sites. DNAse I data is from Joshi et al., 2015.