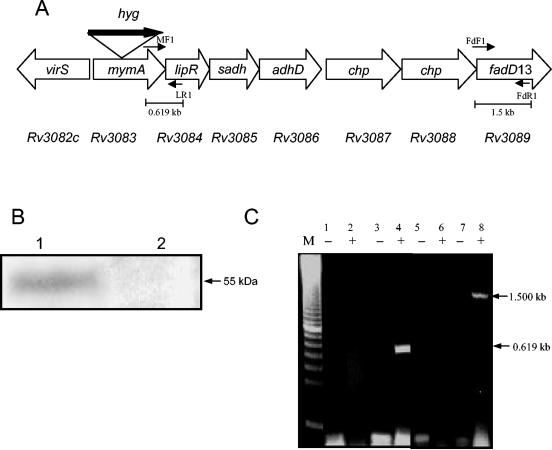
FIG. 1.
(A) Disruption of the mymA (Rv3083) gene of M. tuberculosis. Shown is the schematic organization of the mymA operon of M. tuberculosis with a disrupted mymA (Rv3083) gene. Thick arrow, hygromycin resistance gene, which was used both as a disruption element and as a selection marker. MF1-LR1 and FdF1-FdR1 represent primer pairs used to confirm the effect of disruption on the transcription of downstream genes. Predicted sizes of the amplicons using the primer pairs MF1-LR1 and FdF1-FdR1 are shown. (B) Expression of mymA in M. tuberculosis and Mtbmym::hyg. The cell extract (50 μg protein) from M. tuberculosis (lane 1) and Mtbmym::hyg (lane 2) was resolved on a 10% polyacrylamide gel containing 0.1% SDS and transferred to a Hybond C Extra membrane. The blot was probed using polyclonal antibodies raised in rabbit against MymA. (C) Influence of disruption of mymA on the expression of downstream genes of the mymA operon. RT-PCR products corresponding to mymA-lipR intergenic region and the fadD13 gene were amplified using primer sets MF1-LR1 (lanes 1 to 4) and FdF1-FdR1 (lanes 5 to 8), respectively. In the negative control (−), the PCRs were performed directly on the total RNA isolated from Mtbmym::hyg (lanes 1 and 5) and M. tuberculosis (lanes 3 and 7) to confirm the absence of DNA contamination. RT-PCR was performed on the RNA obtained from Mtbmym::hyg (MF1-LR1, lane 2; FdF1-FdR1, lane 6) and M. tuberculosis (MF1-LR1, lane 4; FdF1-FdR1, lane 8). The size of the PCR product is consistent with the predicted size shown in the figure. M, 100-bp marker (U.S. Biochemicals).