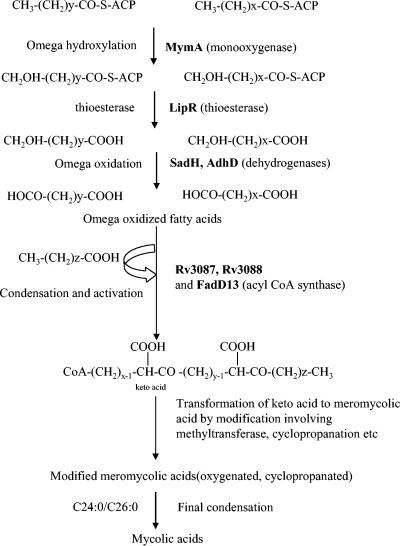
FIG. 10.
Hypothetical scheme showing the involvement of the mymA operon in the biosynthesis of mycolic acids via “head-to-tail” condensation. Biosynthesis of mycolic acids via “head-to-tail” condensation initiates with the omega hydroxylation of the terminal methyl group of two fatty acid molecules (C24:0/C26:0) by MymA (Rv3083), which are converted into a carboxyl group by the dehydrogenases SadH (Rv3085) and AdhD (Rv3085). Release of acyl carrier protein (ACP) esterified to the fatty acid by thioesterase LipR (Rv3084) leads to generation of diacids for the condensation. Head-to-tail condensation by Rv3087 and/or Rv3088 gene products between three fatty acids, two of which are omega oxidized and activation by FadD13 (Rv3089) produce keto acid. The keto acid can then be subjected to functional modification like methylation, cyclopropanation, etc., to produce meromycolic acids which can be condensed to C24:0/C26:0 to produce full-length mycolic acids.