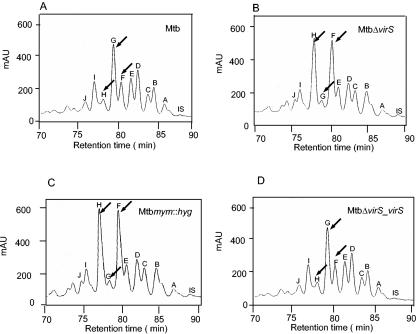
FIG. 3.
Representative HPLC chromatograms of mycolic acids from various strains of M. tuberculosis. M. tuberculosis MtbΔvirS, Mtbmym::hyg, and MtbΔvirS_virS strains were inoculated separately in MB 7H9 medium and grown to an A600 of 1.5. Total fatty acids were extracted, derivatized to UV-absorbing p-bromophenacyl esters, and separated by HPLC as described in Materials and Methods. Shown are mycolic acid profiles of (A) M. tuberculosis, (B) MtbΔvirS, (C) Mtbmym::hyg, and (D) MtbΔvirS_virS from HPLC analysis. Peaks were labeled according to their RRTs. IS, internal high-molecular-weight standard. Arrows indicate the significant differences in the mycolic peaks between various strains.