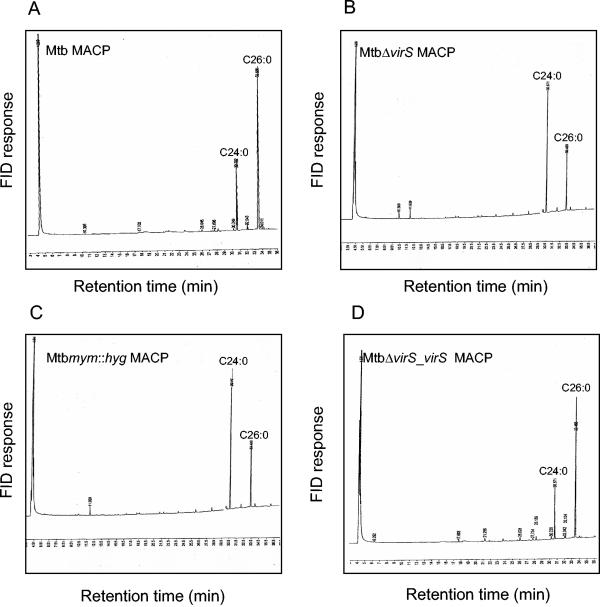
FIG. 7.
Pyrolytic gas chromatography of MAMEs from various strains of M. tuberculosis. The MAMEs from various strains of M. tuberculosis were subjected to thermal cleavage by increasing the injector temperature to 350°C, and the identity of mycolic acid cleavage product (MACP) was confirmed by using an authentic fatty acid methyl ester standard. (A) M. tuberculosis; (B) MtbΔvirS; (C) Mtbmym::hyg; (D) MtbΔvirS_virS. FID and TBS represent flame ionization detector and tuberculostearic acid, respectively.