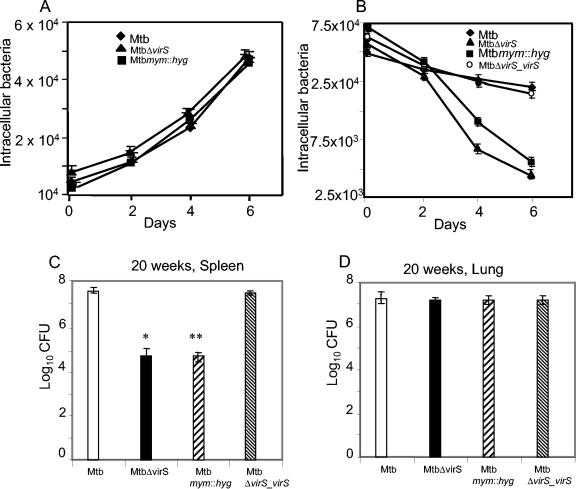
FIG. 9.
Effect of virS and mymA disruption on the in vivo survival of M. tuberculosis in macrophages and guinea pigs. The mouse macrophage cells (J774A.1) were infected with M. tuberculosis, MtbΔvirS, Mtbmym::hyg, and MtbΔvirS_virS strains separately at an multiplicity of infection of 1:10 (macrophage:bacilli). At different time points postinfection (days 0, 2, 4, and 6), macrophages were lysed and the number of intracellular bacilli was assessed by plating on MB 7H10 (A, resting macrophages; B, activated macrophages). The experiment was carried out twice in triplicate, and data depict the means of all six values ± standard errors (SE). Guinea pigs were infected with 5 × 107 CFU of different strains of M. tuberculosis, subcutaneously. Infected guinea pigs (five animals per group at each time point) were euthanized at 10 weeks and 20 weeks postinfection. Spleens and lungs were homogenized in 5 ml of distilled water and 10-fold serial dilutions of the homogenates were plated in duplicate on MB 7H10 medium. Bacillary load in the spleens and lung of guinea pigs euthanized at 20 weeks (C and D, respectively) postinfection is depicted as mean ± SE.