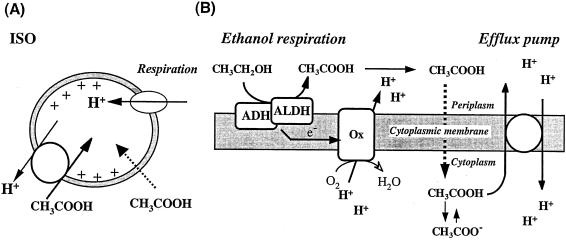
FIG. 8.
Schematic representation of acetic acid uptake in ISO membrane vesicles and model of the efflux pump present in the cytoplasmic membrane of A. aceti. (A) ISO membrane vesicles generate a proton motive force, inside positive and acidic, by respiration (lactate oxidation), which then drives acetic acid uptake. The stoichiometry of protons and acetic acid in the pump is unknown. There is also a passive diffusion of acetic acid, which is ΔpH dependent. (B) In intact cells, ethanol respiration produces acetic acid from ethanol via the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), which also donate electrons to a terminal ubiquinol oxidase (Ox) that in turn generates a proton motive force. The acetic acid produced can passively penetrate into the cytoplasm but is pumped out by an efflux pump which is energized by the proton motive force.