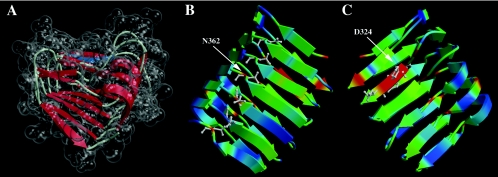
FIG. 3.
Three-dimensional model of AlgG from amino acids G286 to A434, showing six rungs of the right-handed β-helix. (A) The model of the RHβH is shown with the transparent space-filling representation encasing schematically drawn secondary-structure elements. This view positions the shallow groove associated with β-sheet 1 (PB1), the putative catalytic face of RHβH proteins, at the top of the molecule. Shown in blue is the 324-DPHD motif that is required for mannuronan epimerase activity. (B) View of AlgG showing turn region T2 and its associated asparagine stacking. Colors correspond to residue conservation among AlgG homologs, with red denoting the most conserved amino acid residues within the AlgG family and blue indicating the least conserved residues. Asparagine residues are shown in the ball-and-stick representation. (C) Rotation (180° around the y axis) view of AlgG showing β-sheet 1 (PB1) that contains the 324-DPHD motif, shown in the ball-and-stick representation. Color coding is based on amino acid conservation as in B.