Figure 1.
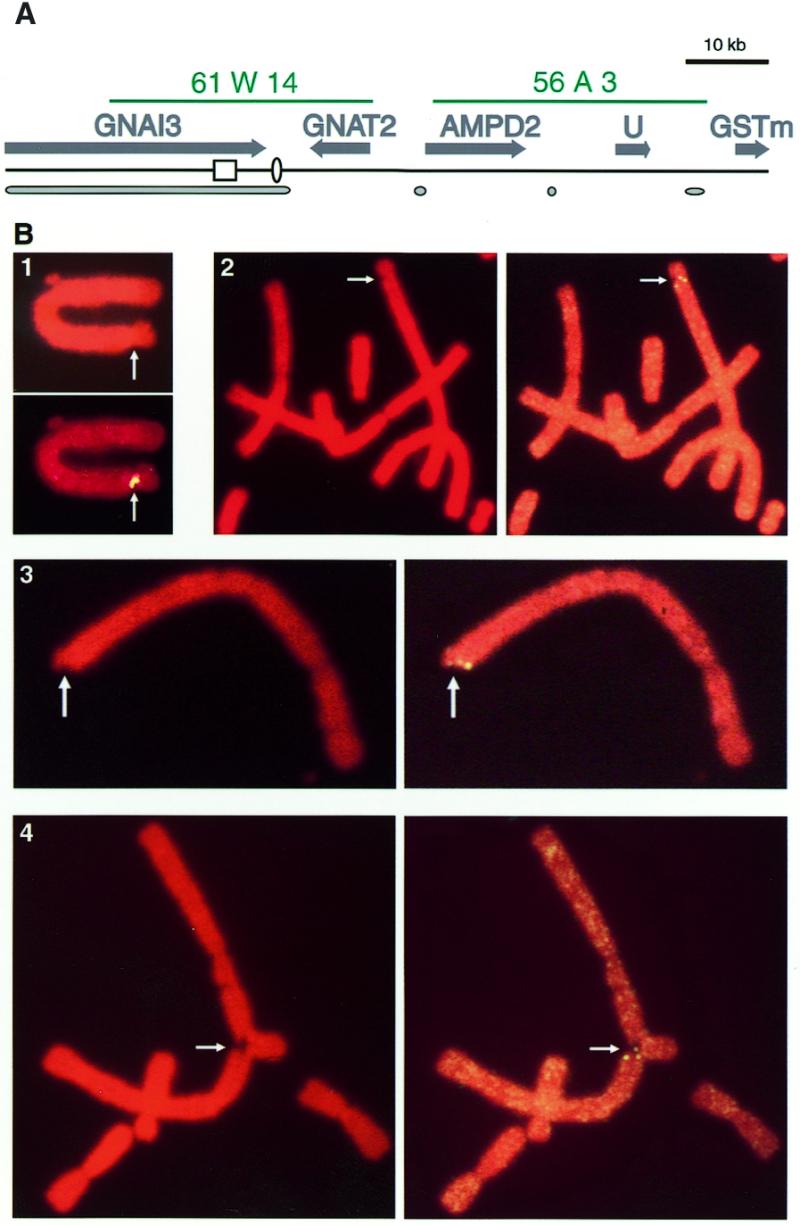
Aphidicolin induces recurrent breaks in the Chinese hamster GNAI3–GNAT2 region. (A) Map of the analysed regions. From top to bottom are shown cosmid probes used in this study (in green), genes (grey arrows, transcription directions), the hot spot for recombination (open box) and the DNA replication origin oriGNAI3 (open oval), putative MARs (grey ovals). (B) Examples of aberrant hybridisation signals observed with a 61 W14 biotinylated probe following aphidicolin treatment. 1, Croissant-shaped hybridisation signal colocalised with an aphidicolin-induced chromosome constriction. 2 and 3, Split signals colocalised with aphidicolin-induced single chromatid breaks. 4, Split signal colocalised with an interchromosomal rearrangement. Propidium iodide staining, top (1) or left (2–4); FISH with a 61 W14 biotinylated probe, bottom (1) or right (2–4).
