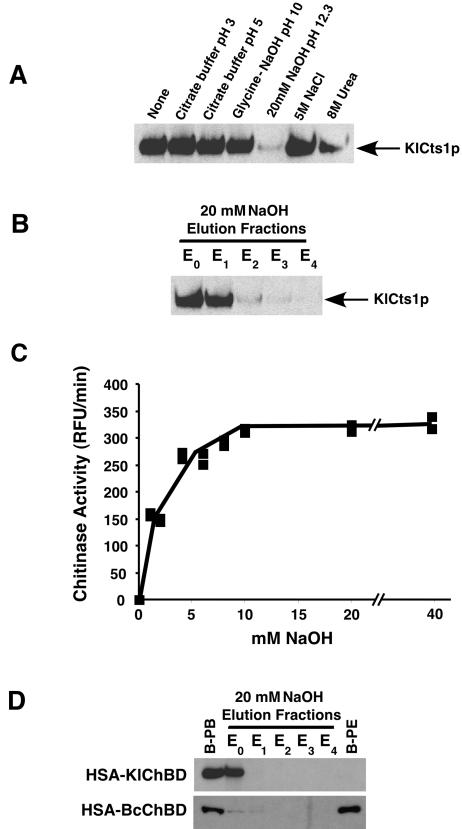
FIG. 4.
KlCts1p dissociates from chitin at high pH. (A) KlCts1p was bound to chitin beads in minicolumns as described in Materials and Methods. The solutions were passed over separate minicolumns, after which KlCts1p that was still chitin bound was eluted by boiling, separated by SDS-PAGE, and detected by α-ChBD Western blotting. (B) KlCts1p elution from chitin with 20 mM NaOH. Chitin-bound KlCts1p was eluted in five successive 1-ml fractions of 20 mM NaOH (E0 to E4, where E0 represents the column void volume), separated by SDS-PAGE, and detected by α-ChBD Western blotting. (C) Base-eluted KlCts1p retains chitinolytic activity. Chitin-bound KlCts1p was eluted from chitin with various concentrations of NaOH, and the eluates were assayed for chitinase activity with 4MU-GlcNAc3 at pH 4.5 and 37°C. RFU, relative fluorescence units. (D) KlCts1p-ChBD can function as an elutable affinity tag. HSA fusions to ChBDs derived from KlCts1p or B. circulans ChiA1 were secreted from K. lactis, bound to chitin beads, and eluted with five 1-ml 20 mM NaOH fractions (E0 to E4). Proteins that were bound to chitin beads prior to elution (B-PB) or that were still bound after elution with 20 mM NaOH (B-PE) were eluted by boiling. All samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and examined by α-ChBD Western blotting.