FIG. 4.
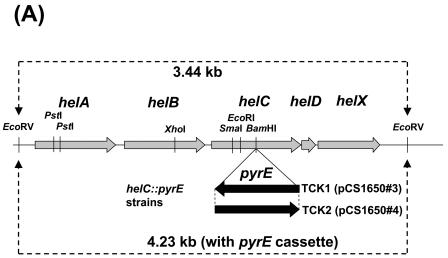
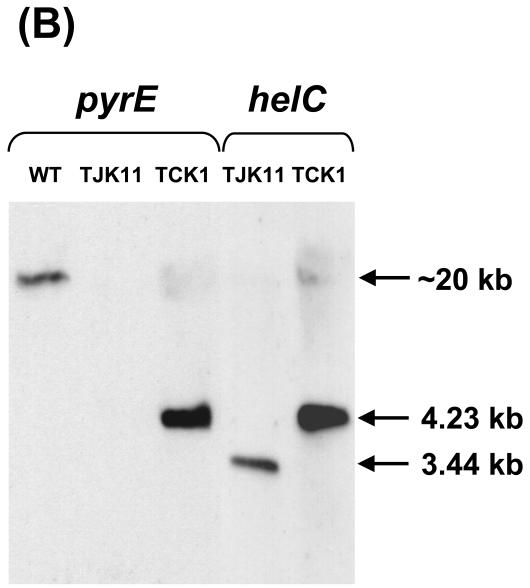
Southern hybridization analyses of the helC::pyrE mutants TCK1 and TCK2. (A) Physical map of the hel gene cluster of the helC::pyrE constructs. Wild-type chromosomal DNA digested with EcoRV generated a 3.44-kb DNA fragment that contained the entire helABCDX gene cluster. In helC::pyrE mutants TCK1 and TCK2, the pyrE gene cassette was inserted at a unique BamHI site of helC in opposite orientations, as indicated by the solid arrows. In these mutant strains, EcoRV digestion generated a 4.23-kb DNA fragment containing the entire helABCDX gene cluster and the inserted pyrE gene cassette. The restriction enzyme recognition sites for BamHI, EcoRI, EcoRV, PstI, SmaI, and XhoI are indicated. (B) Southern hybridization analyses of R. capsulatus wild type (WT), the PyrE− mutant TJK11, and the HelC null mutant TCK1. Genomic DNA isolated from MT1131, TJK11, and TCK1 were digested with EcoRV, and the digests were analyzed by using DIG-labeled pyrE and helC gene probes. The molecular sizes of the positive blots are indicated. The high-molecular-weight band (∼20 kb) in the wild-type lane corresponds to the chromosomal pyrE locus.