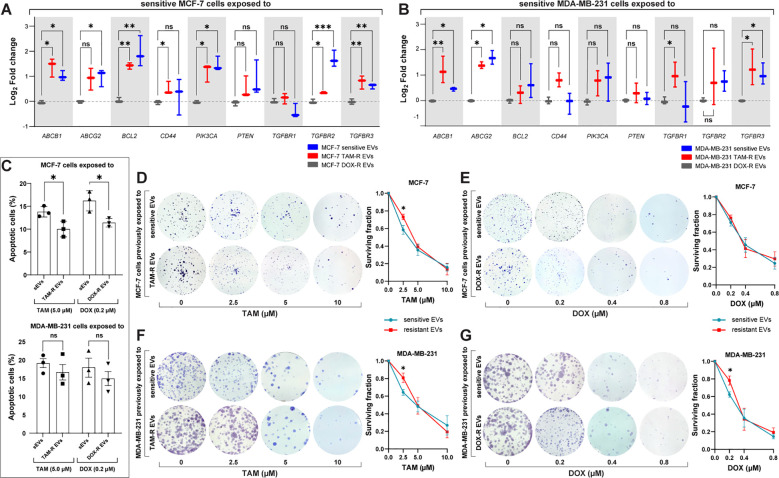
Figure 6.
Resistant extracellular vesicles (EVs) induce the upregulation of genes associated with acquired drug resistance and increase the sensitive cells’ survivability. The quantification of several genes by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) of (A) sensitive MCF-7 exposed to tamoxifen-resistant (TAM-R) and doxorubicin-resistant (DOX-R) EVs. (B) The gene expression level of sensitive MDA-MB-231 cells exposed to TAM-R and DOX-R. (C) The apoptotic rate by annexin V/propidium iodide labeling in sensitive MCF-7 and sensitive MDA-MB-231 previously exposed to resistant EVs and treated with TAM and DOX. (D) Representative images and the clonogenic surviving fraction of MCF-7 cells previously exposed to TAM-R and (E) DOX-R EVs treated with the respective drug. (F) Representative images and the clonogenic surviving fraction of MDA-MB-231 cells previously exposed to TAM-R and (G) DOX-R EVs treated with the respective drug. Values are displayed as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate a significant difference between TAM-R EVs or DOX-R EVs exposure compared to sensitive EV effects (unpaired t-test). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns, not significant.