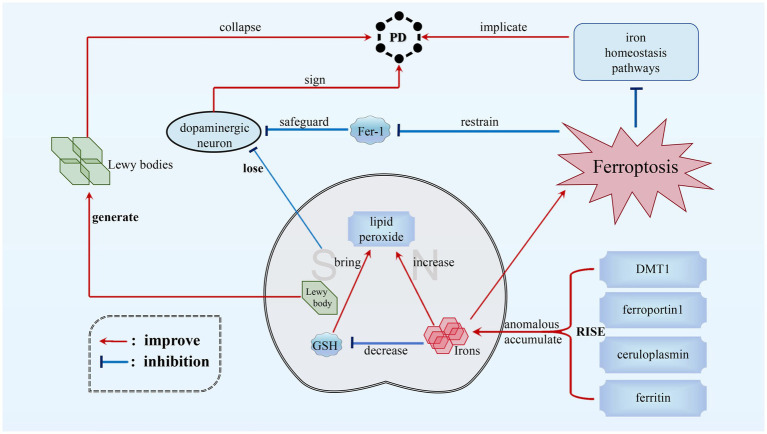
Figure 3.
Ferroptosis in PD. The main pathological features of PD are the significant increase in Lewy bodies within the gray matter and the reduction in dopaminergic neurons. The destruction of dopaminergic neurons can be caused by neurotoxins produced by ferroptosis. This process disrupts iron homeostasis pathways and alters the function of ceruloplasmin. Furthermore, it increases the expression of ferroportin1 and DMT1, as well as ferritin levels. These changes result in abnormal iron accumulation in the substantia nigra (SN), ultimately leading to ferroptosis and creating a vicious circle. However, the compound Fer-1 has the ability to protect dopaminergic neurons and inhibit ferroptosis, thereby reducing the severity of PD.