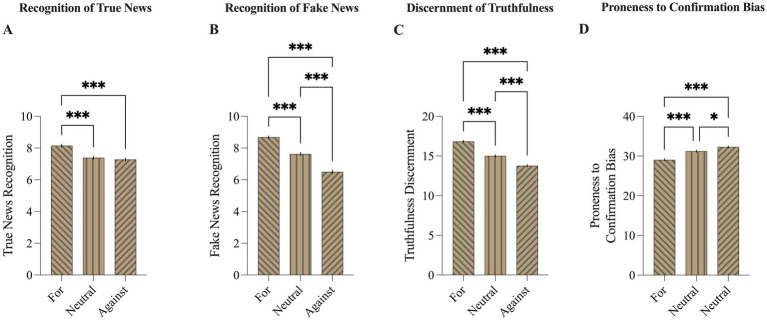
Figure 3.
Comparison of susceptibility to true and fake news, and proneness to confirmation bias between COVID-19 vaccine opinions groups. Participants, categorized according to their opinions about COVID-19 vaccines, differed in their abilities to recognize (A) true news, (B) fake news, and (C) discernment of truthfulness. Additionally, variations were observed in their susceptibility to confirmation bias (D) – those opposed to vaccines were most prone to this bias. Means are presented with ± SEM; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.