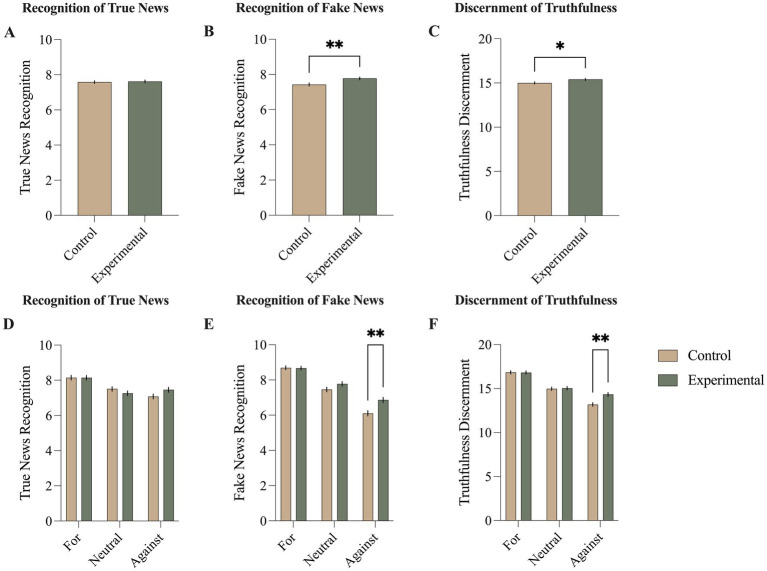
Figure 4.
The impact of confirmation bias awareness on susceptibility to true and fake news. The control and experimental groups did not significantly differ in the average recognition of true news (A). Significant differences were observed in the recognition of fake news (B) and discernment of truthfulness (C). Adding the attitude towards COVID-19 vaccines factor, resulted in no significant interactions in recognition of true news (D). However, the experimental group with a negative attitude towards COVID-19 vaccines, presented better recognition of fake news (E) and a higher ability to discern truthfulness (F), when compared to the control group with such an attitude. Mean ± SEM; * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01.