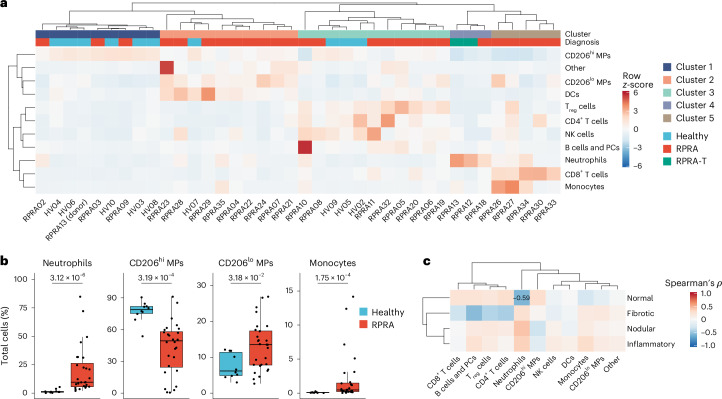
Fig. 2. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages and neutrophils are expanded in patients with RPRA compared with healthy volunteers.
a, Hierarchical clustering of flow cytometry data from BAL fluid samples from patients with RPRA (n = 26), patients with RPRA who subsequently underwent a lung transplantation (n = 2) and healthy controls (n = 10). One of the patients with RPRA who subsequently required a lung transplantation had BAL fluid obtained from each lung separately. Clustering was performed using Ward’s method. Rows are z-scored. CD206hi or CD206lo macrophage (CD206hi or CD206lo MP), plasma cells (PCs). b, Proportions of significantly differentially abundant cells measured by flow cytometry from the same BAL fluid samples as in a (q < 0.05, pairwise Wilcoxon’s rank-sum tests with FDR correction). Padj values are shown above each pair of boxplots. c, Hierarchical clustering of correlation coefficients (Spearman’s ρ) between cell-type abundances measured by flow cytometry in patients with RPRA (n = 28) and the features identified in their CT scan 1 as in Fig. 1c. Clustering was performed using Ward’s method. Correlation coefficients are shown only when the association was significant (q < 0.05, permutation tests with FDR correction).