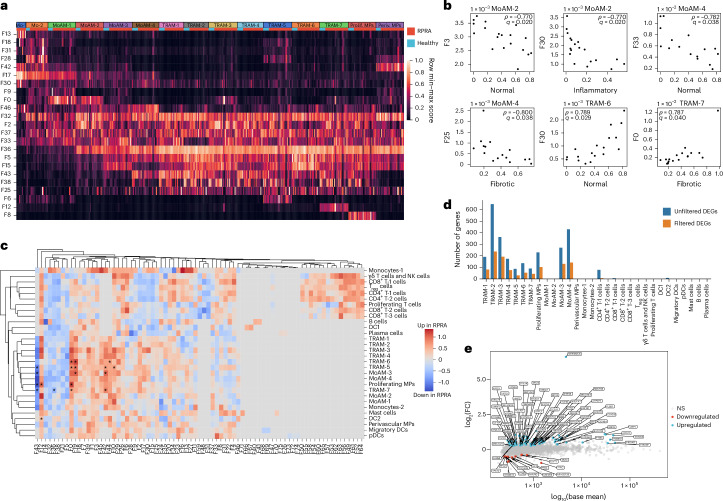
Fig. 4. Gene programs associated with pulmonary fibrosis in monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages are associated with radiographic abnormalities in patients with RPRA.
a, Heatmap of scores for selected Spectra programs within monocyte (Mo-1 and Mo-2) and macrophage clusters (MoAM-1 to MoAM-4; TRAM-1 to TRAM-7; proliferating MPs (prolif. MPs) and perivascular MPs (periv. MPs)) identified in BAL fluid scRNA-seq data from patients with RPRA (n = 24) and healthy controls (n = 6) as in Fig. 3a. Each column represents a single subject. Rows are scaled minmum to maximum (min–max). b, Correlations (Spearman’s ρ) between Spectra participant scores and CT features in MoAM-2 and MoAM-4 and TRAM-6 and TRAM-7, as in Fig. 3a. Only significant associations are shown (q < 0.05, permutation tests with FDR correction). Padj values and correlation coefficients are annotated on each plot. c, Hierarchical clustering on the signal/noise ratio of Spectra participant scores between patients with RPRA (n = 24) and healthy controls (n = 6). Factors that are differentially expressed (q < 0.05, Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test on subject scores with FDR correction) are indicated with an asterisk. d, Barplot showing the number of DEGs between different cell types in the BAL fluid in patients with RPRA (n = 24) and healthy controls (n = 6) (q < 0.05, Wald’s test with FDR correction) with and without filtering criteria applied for DEGs. e, DEGs in TRAM-1 cluster. FC, fold-change; NS, not significant (q > 0.05).