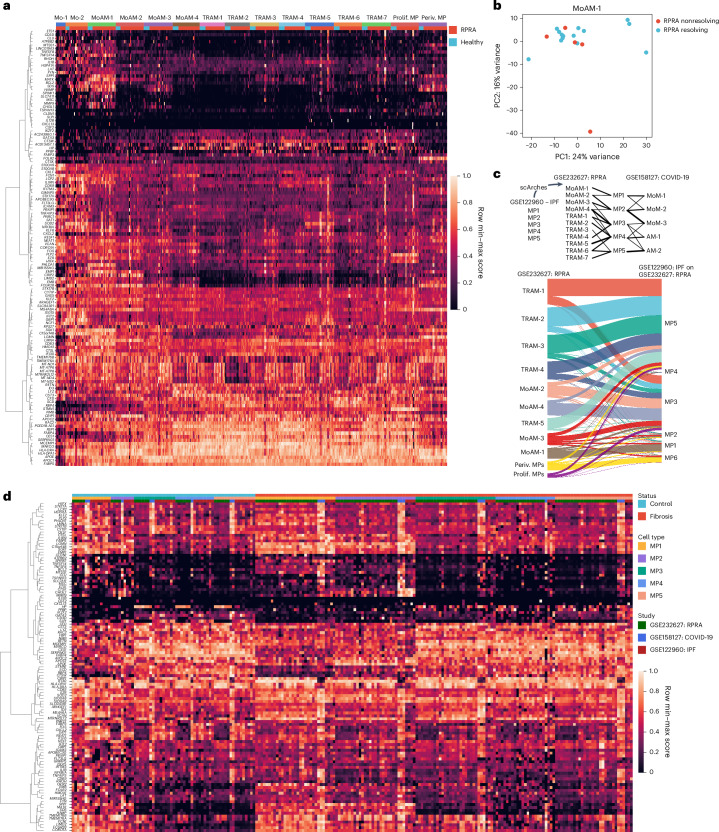
Fig. 5. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages show similar transcriptomic signatures in patients with resolving or nonresolving RPRA.
a, Expression of genes from Spectra programs F0, F5, F9 and F43 within monocyte (Mo-1 and Mo-2) and macrophage clusters (MoAM-1 to MoAM-4, TRAM-1 to TRAM-7, prolif. MPs and periv. MPs) identified from BAL fluid scRNA-seq data of patients with RPRA (n = 24) and healthy controls (n = 6) as in Fig. 3a. Each column represents a single subject. Genes with weights >0.0002 were retained. Rows are scaled minimum to maximum and hierarchically clustered. b, Principal component analysis (PCA) of pseudobulk gene expression in cluster MoAM-1 from patients with resolving (n = 15) and those with nonresolving (n = 5) RPRA as defined by serial CT scans of the chest. c, Top, schematic of transfer learning approach to harmonize macrophage labels across three datasets in which the scArches model was trained on scRNA-seq data from patients with IPF and lung transplant donors (GEO accession no. GSE122960) and labels projected on to data from the present study (accession no. GSE232627) and data from patients with end-stage pulmonary fibrosis secondary to COVID-19 and two controls (accession no. GSE158127). Bottom, Sankey diagram illustrating mapping of macrophage cluster labels identified in the patients with RPRA in the present study (accession no. GSE232627; n = 24) and labels transferred from patients with IPF (n = 4) and donor lungs (controls, n = 8) (accession no. GSE122960). d, Combined heatmap showing expression of genes from Spectra programs F0, F5, F9 and F43 in alveolar macrophages from patients with RPRA in the present study (accession no. GSE232627; n = 24), patients with IPF (n = 4) and donor lungs (controls, n = 8) (accession no. GSE122960), and patients with end-stage pulmonary fibrosis secondary to COVID-19 (n = 3) and donor lungs (controls, n = 2) (accession no. GSE158127). Columns are organized by disease status, macrophage subsets (MP1 to MP6) and dataset (RPRA, IPF and COVID-19-induced lung fibrosis). Genes with weights >0.0002 were retained. Rows are scaled minmum to maximum and are hierarchically clustered.