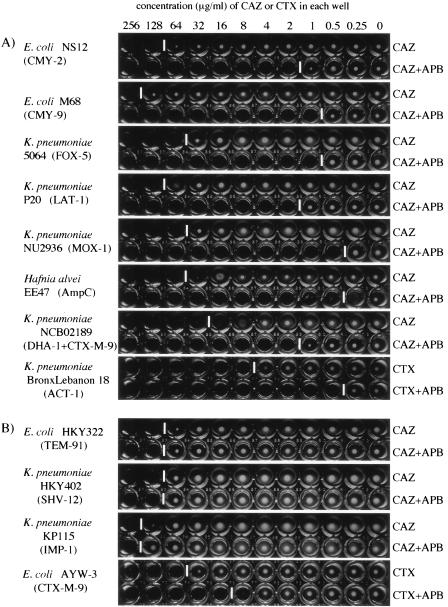
FIG. 3.
Microdilution test with APB for detection of class C β-lactamases. APB was added to serial dilutions of CAZ or CTX, and the concentration of ABP in each well is 300 μg/ml. (A) Detection of plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases in representative E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates and chromosomal AmpC β-lactamase in H. alvei EE47. An eightfold or greater decrease in the MIC of CAZ or CTX with the addition of APB is indicative of the production of class C β-lactamases. (B) Negative results of microdilution test by using APB for E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates producing class A ESBLs or a class B MBL, IMP-1. Among the strains tested, the level of resistance to cefotaxime was reduced in the presence of APB in a few strains, such as CTX-M-9-producing E. coli AYW-3; and the coproduction of chromosomal AmpC was suspected in this strain. It may even be possible to distinguish strains that chiefly produce a class A or a class B enzyme, together with a small amount of a class C enzyme, from those that mainly produce class C enzymes when the breakpoint was set at a decrease in the MIC of greater than or equal to eightfold (three tubes) in the presence of APB. White vertical bars between the wells indicate the upper limit of bacterial growth in each line.