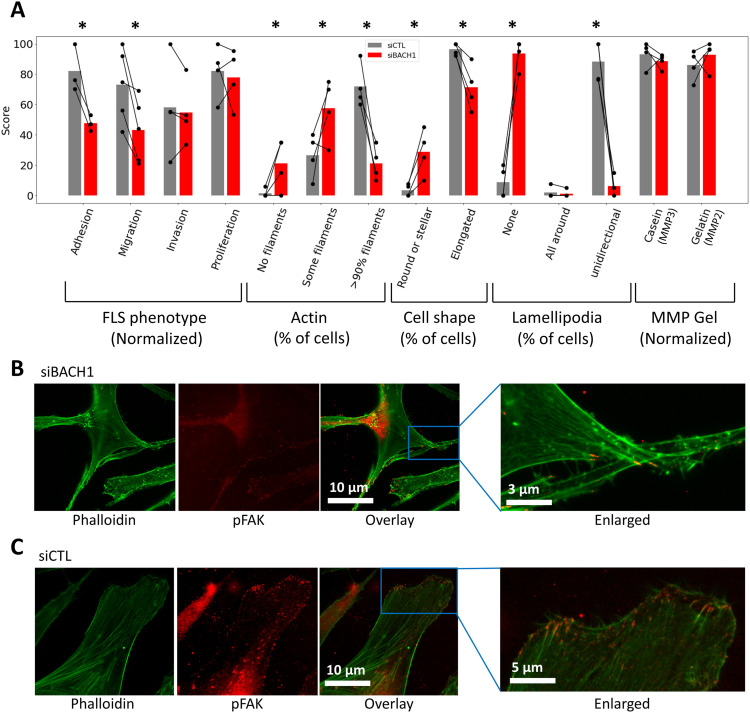
Figure 6. BACH1 silencing and changes in RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS).
(A) BACH1 silencing reduced RA FLS adhesion and migration (wound healing assay), and affected cell morphology, including key characteristics required for movement and invasion such as thick and linear visible actin filaments (77), elongated shape, and the unidirectional formation of lamellipodia (bars represent the mean of each phenotype in each group; *P < 0.05, paired t test). Phenotype scores on the y-axis were quantified either by the % of cells with the described attribute, or by dividing the score by the highest measured value and multiplying by 100 (indicated as normalized). (B, C) Representative immunofluorescence microscopy images of RA FLS (magnification 500x), showing actin fibers and lamellipodia, marked by phalloidin and pFAK, respectively. (B, C) FLS were treated with (B) siRNA BACH1, showing a stellate morphology, with disorganized actin fibers and no lamellipodia, whereas (C) cells treated with siRNA control (CTL) had the typical RA FLS elongated morphology with thick and organized actin fibers, as well as polarized formation of lamellipodia.