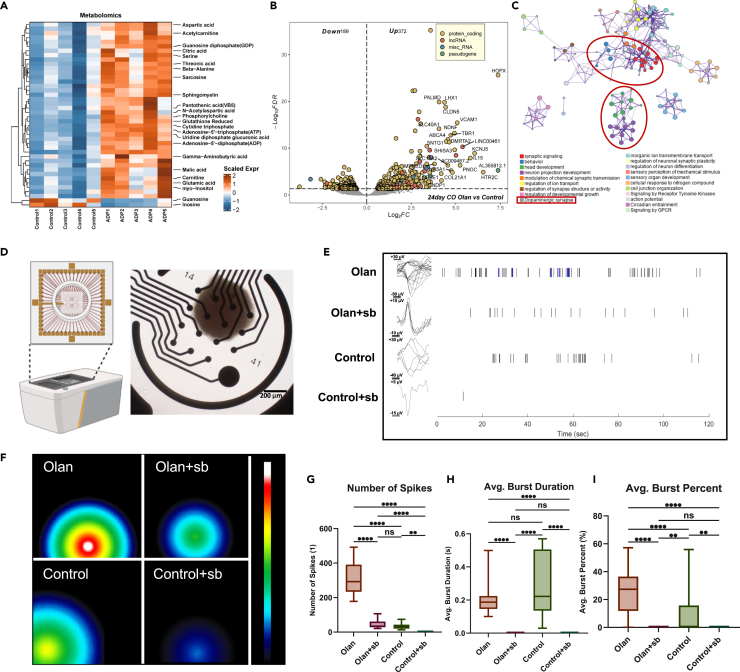
Figure 5.
Early surging of NODAL signaling is essential to the later formation of functional neural networks in CO
(A) Heatmap showing the important metabolites that differed between the olanzapine-treated and control CO group on day 24. Data were scaled before visualization.
(B) Volcano plot showing the DEGs in the olanzapine-treated group compared with the control group on day 24. FDR< 0.05.
(C) PPI network analysis was conducted to determine the intimacy of each gene annotation term in 24-day olanzapine-treated CO.
(D) Diagram of MEA assay of this study. COs were placed in the middle of the opening in the CytoView MEA 24 (Axion BioSystems, Inc.), which was covered by 16 electrodes at the bottom. The whole orifice was then placed in the Maestro Edge (Axion BioSystems, Inc.) for discharge detection.
(E) Representative signals of spike recording the single neuronal discharge of CO in the olanzapine-treated (Olan), olanzapine+SB431542 dual-treated (Olan+sb), control, and SB431542 single-treated (Control+sb) groups. The blue signals refer to a burst, a discharge mode that appears in consecutive discharge and resting periods.
(F) Representative heatmap showing the maximal discharge intensity of each CO in the Olan, Olan+sb, N, and N + sb groups. Different locations of signal refer to different electrodes that detected the signals.
(G–I) Boxplot showing the number of spikes (G), the average burst duration (H) and the average burst percentage in all the neuronal discharge (I) of COs in the Olan, Olan+sb, N, and N + sb groups. The number of spikes was counted each in a 2-min recording. At least 3 organoids (only hiPSC-U2 cell line) for each group were included. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison adjustment. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ns: p > 0.05. Data are represented as median ± IQR. (Detailed statistical data can be found in Table S11).