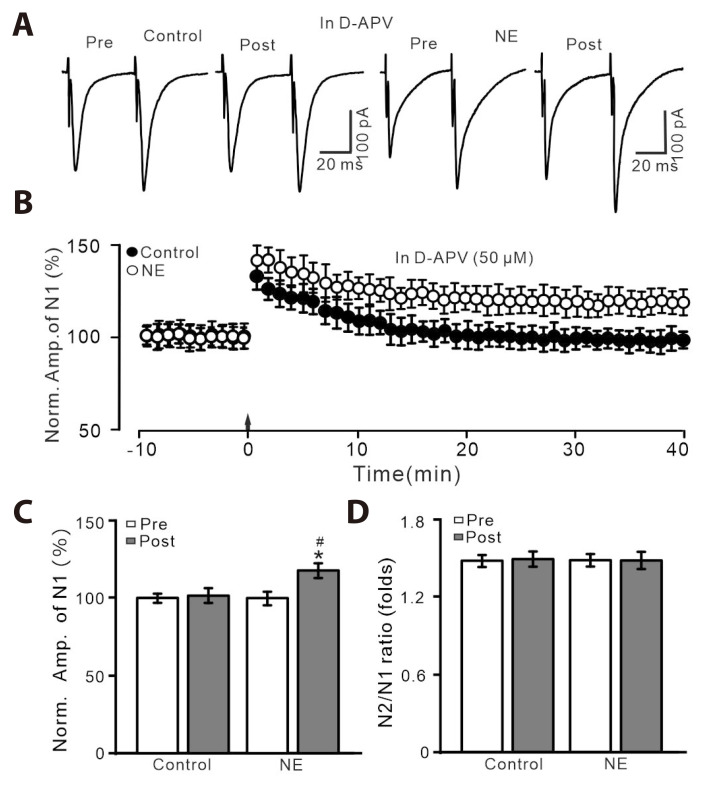
Fig. 2. HFS-induced LTP was abolished by an NMDAR blocker, D-APV, but it was rescued by the application of NE.
(A) In the presence of D-APV (50 µM), representative whole-cell recording traces showing paired-pulse stimulation (duration: 0.2 msec, interval: 50 msec) evoked EPSCs in PVN MNCs before (pre), after (post) delivering HFS in treatment with ACSF (control; left) and NE (100 nM; right). (B) Pooled data showing the time course of the normalized amplitude of N1 before and after delivery of HFS (arrow head) during treatment with ACSF and NE. (C, D) Bar graphs show the normalized amplitude of N1 (C) and N2/N1 ratio (D) in each group, before (pre) and after (post) delivery of HFS. HFS, high frequency stimulation; LTP, long-term potentiation; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors; D-APV, D-(-)-2-Amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid; NE, norepinephrine; EPSCs, excitatory postsynaptic currents; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; MNCs, magnocellular neuroendocrine cells; ACSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid. *p < 0.05 vs. pre; #p < 0.05 vs. post of control; n = 7 cells from 6 mice in each group.